Project management from theory to practice
Theory introduction
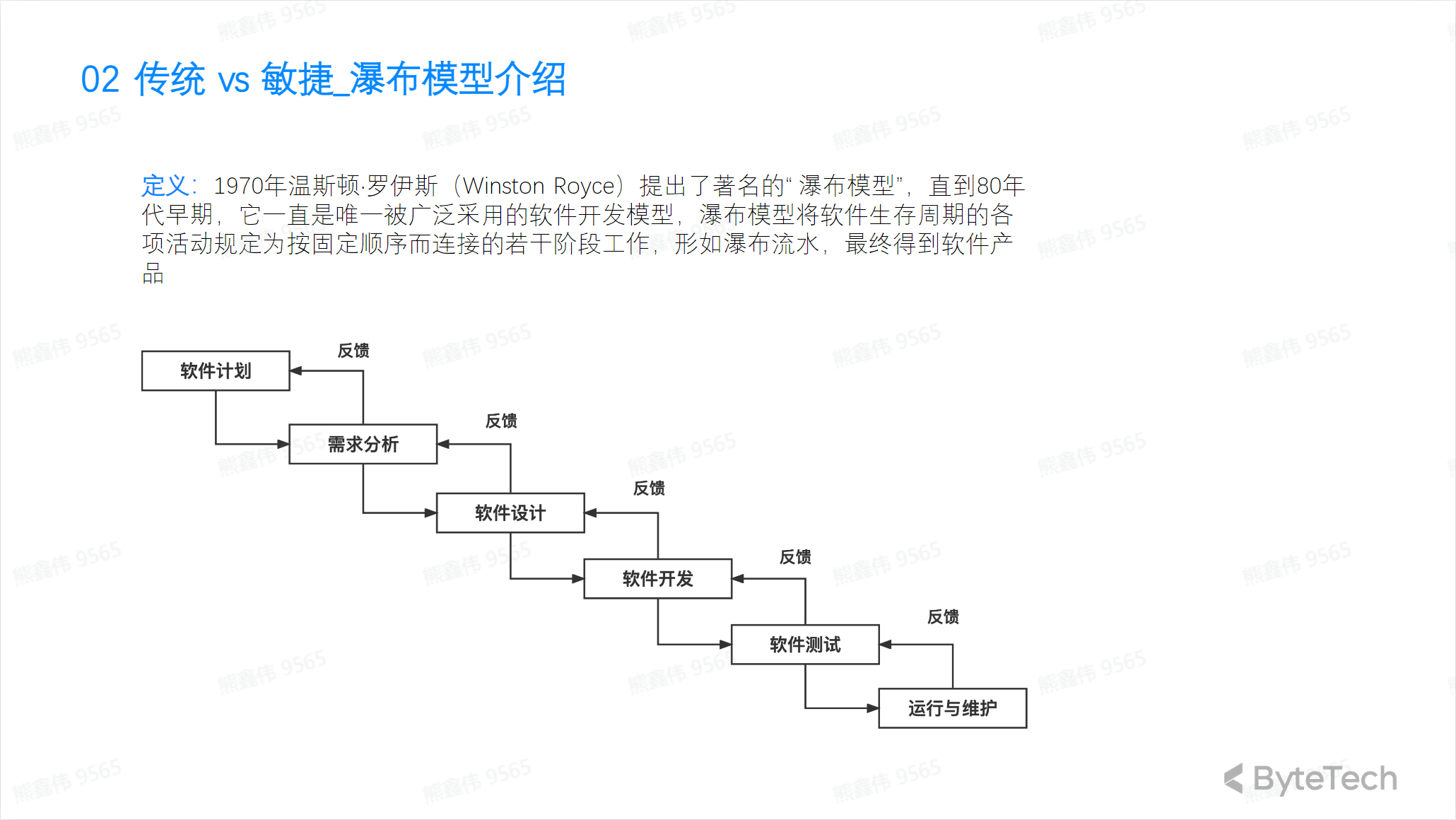
Waterfall Model:
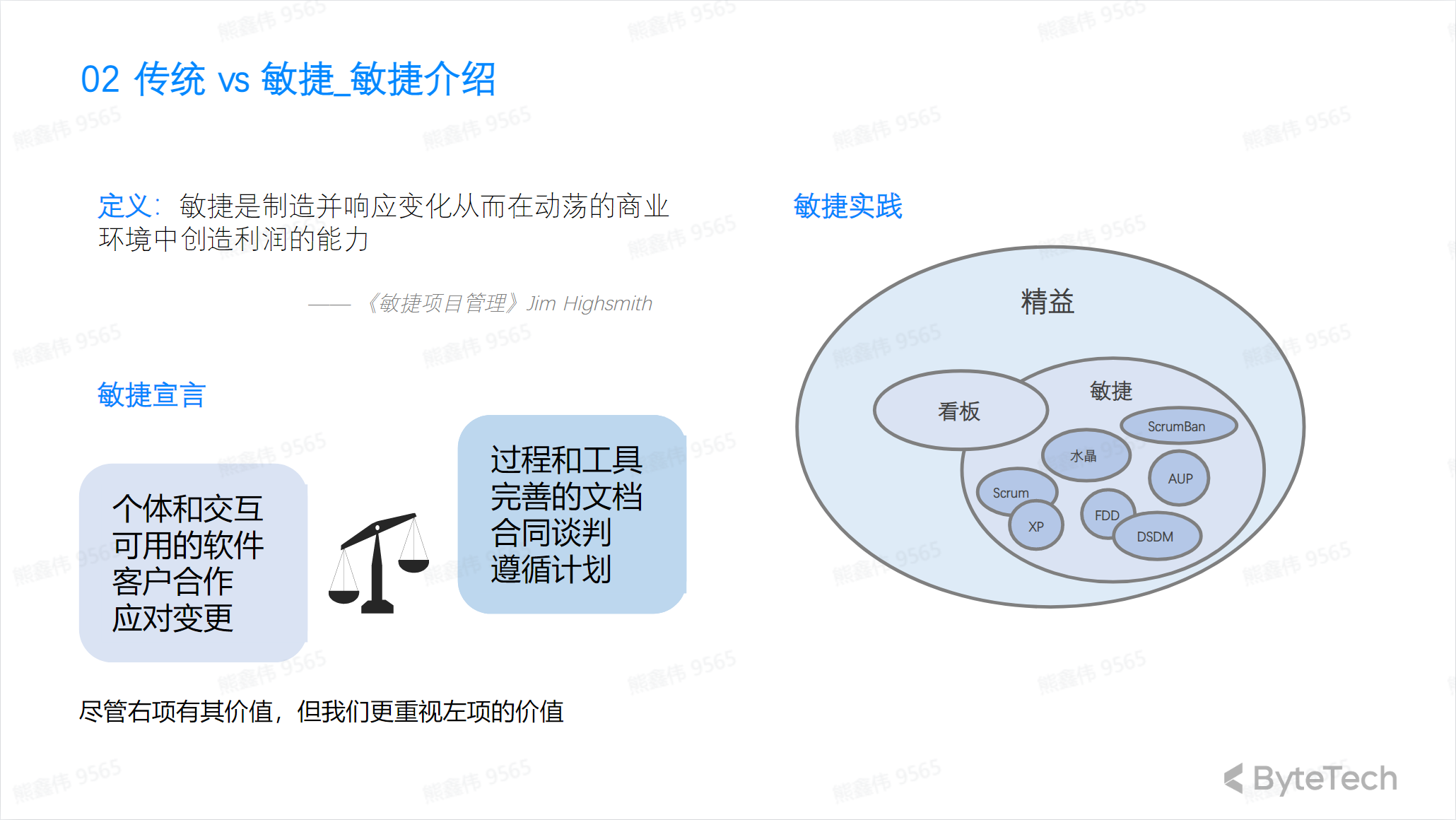
Agile Model:
Scrum Framework:

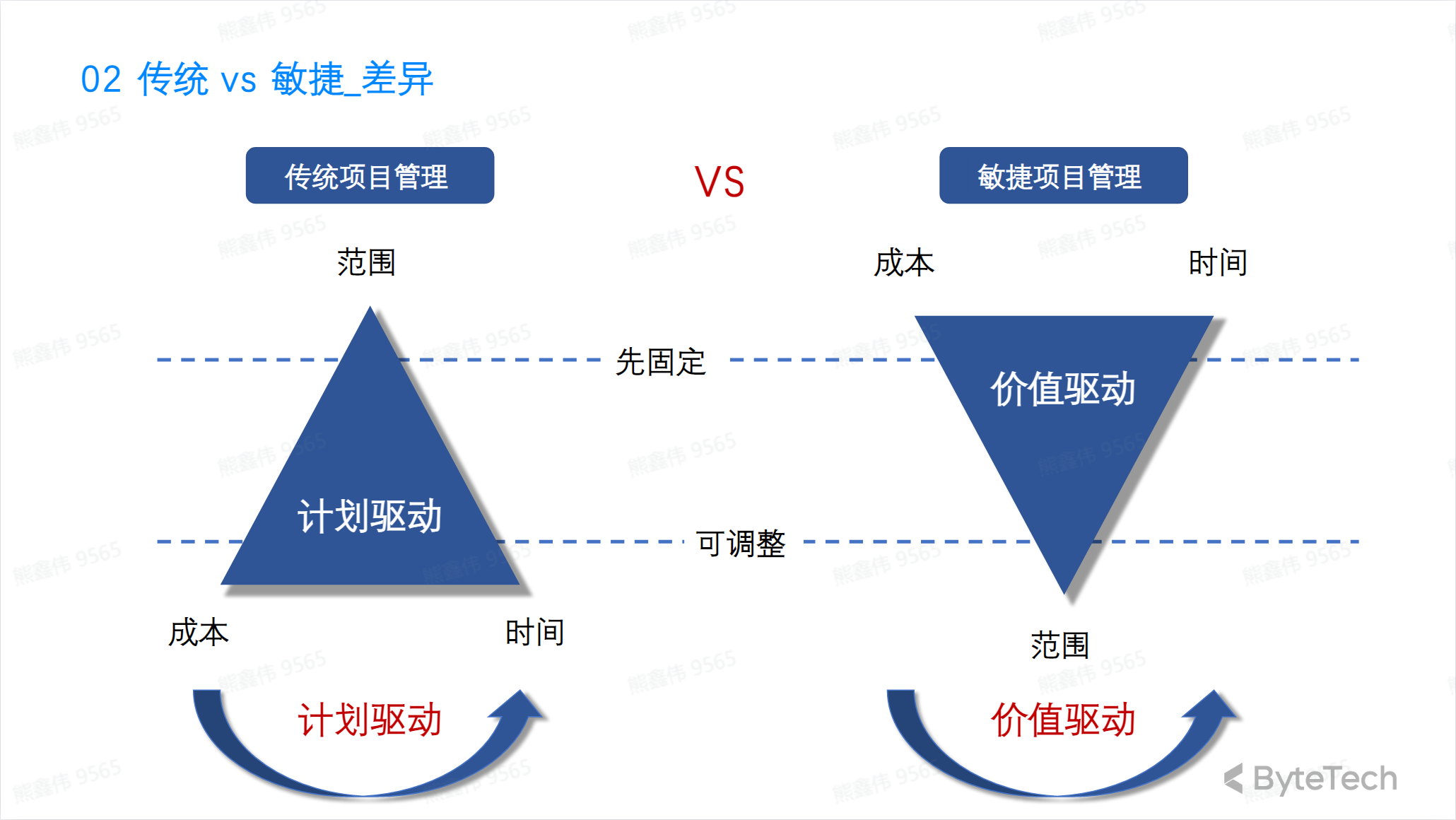
Differences between traditional and agile
**Traditional project management methods typically follow a linear process, achieving project goals through pre-established planning, supervision, and control. Agile project management methods are more flexible and achieve project goals through iteration and continuous improvement. Agile methods emphasize teamwork, adapting to changes, and delivering value quickly. **
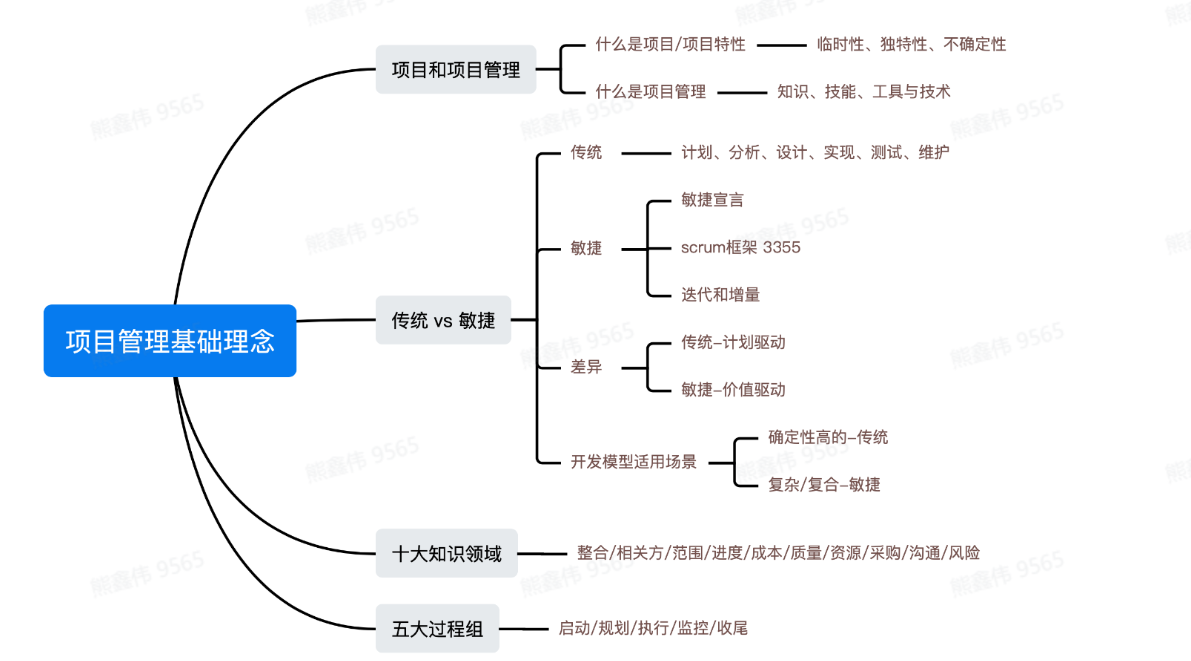
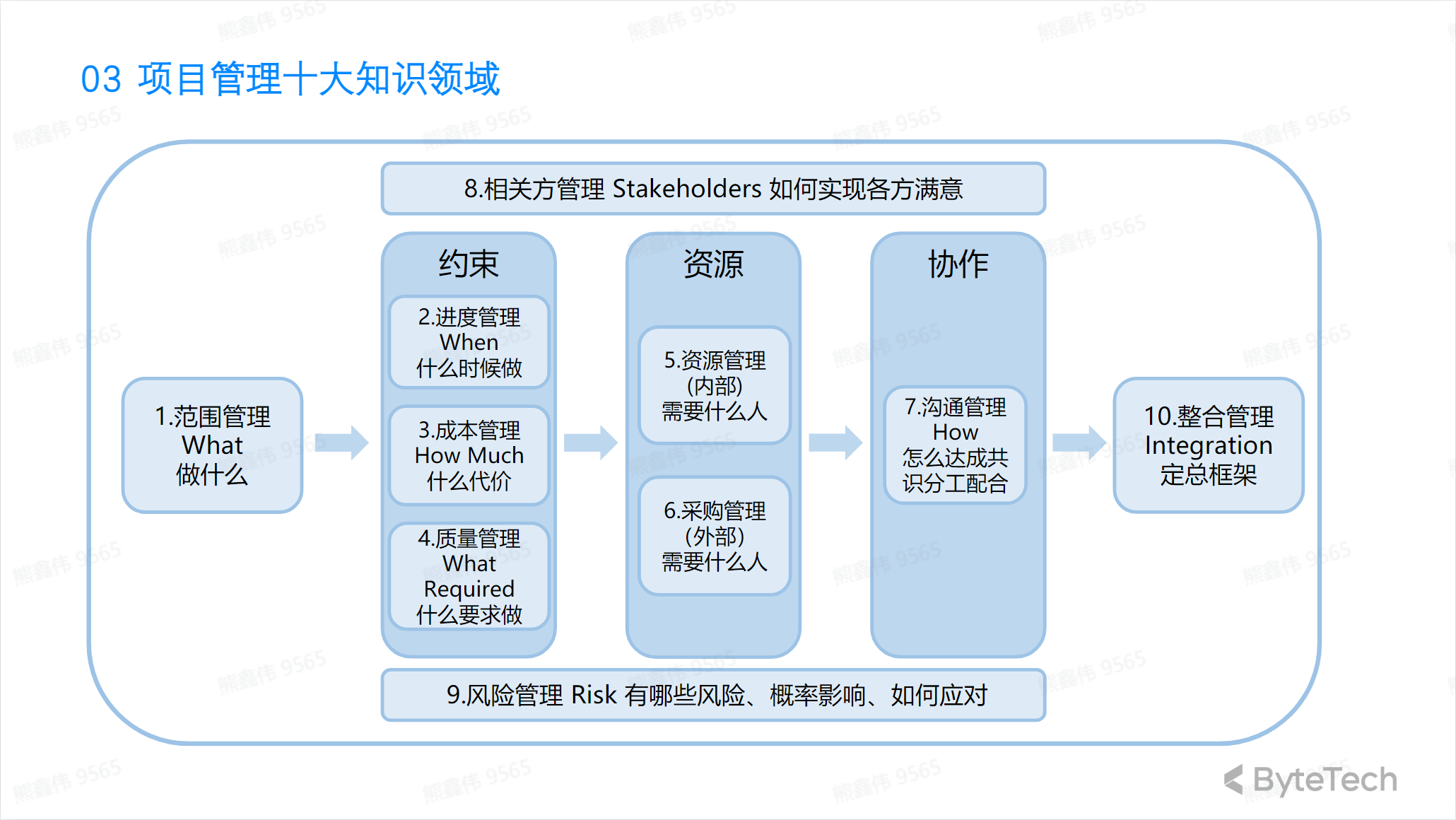
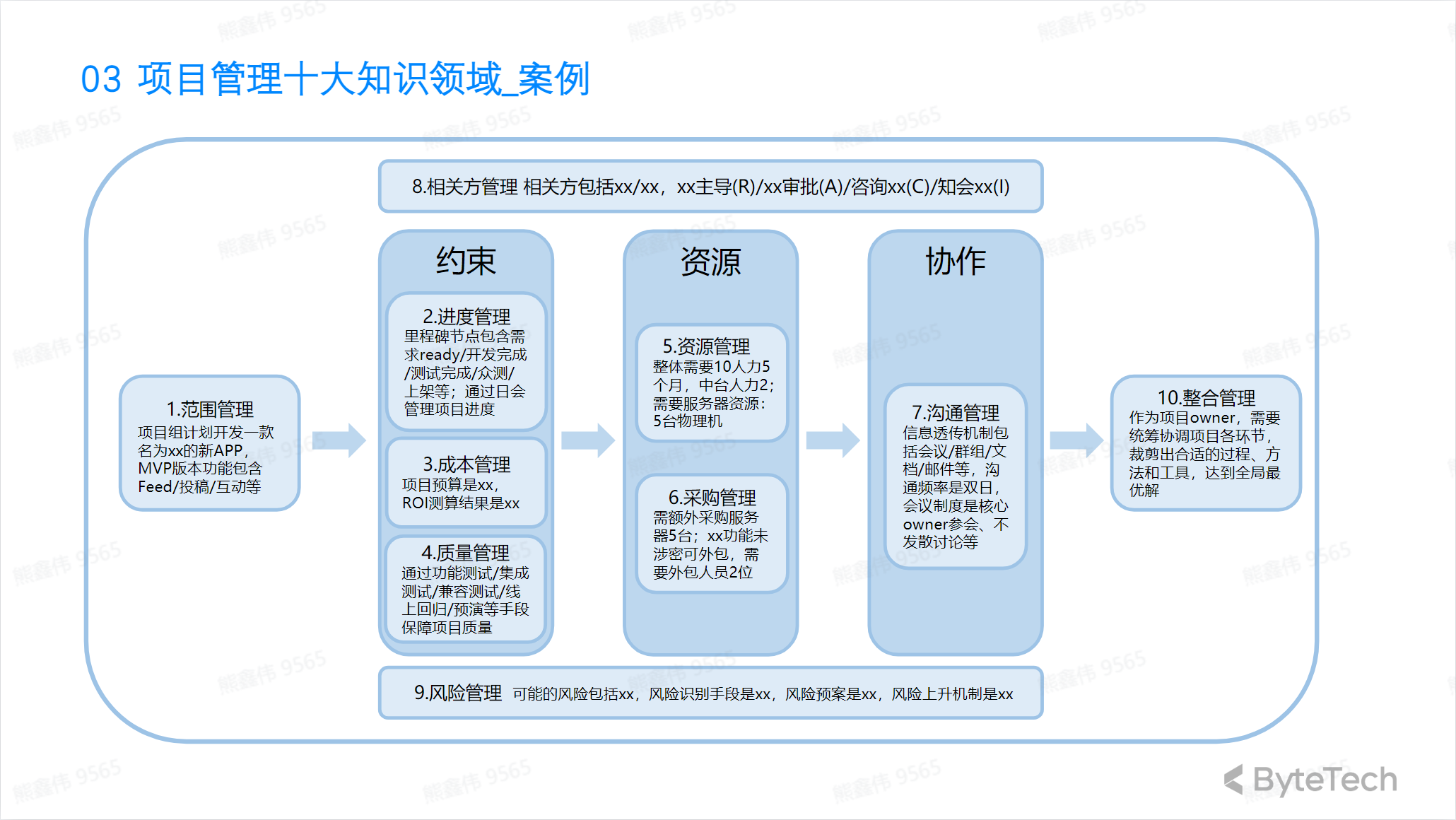
Top ten knowledge areas of project management
The ten knowledge areas of project management include:
- Project scope management: Determine the goals and boundaries of the project and ensure that the project does not exceed these scopes during the process.
- Project time management: Determine the project time plan and ensure the project is completed on time.
- Project cost management: Determine the project budget and ensure that the project is completed within the budget.
- Project quality management: Ensure that project products, services or results meet quality standards.
- Project resource management: Determine the personnel, equipment and materials required for the project and ensure that these resources are used effectively.
- Project communication management: Determine the information needs of the project and ensure that project information is effectively transmitted.
- Project risk management: Identify, assess and respond to risks in projects.
- Project Procurement Management: Determine the external products, services or results required for the project and ensure that these external elements are effectively managed.
- Project contract management: Manage contracts in the project, including signing contracts, supervising contract performance and ending contracts.
- Project completion management: Record project results and evaluate the project to determine improvement points for future projects.
Five process groups of project management
The five process groups of project management are:
- Initiation process group: Activities performed before project initiation, including determination of project scope, goals, budget, and resources.
- Planning Process Group: Develop plans for project success, including project time, cost, quality, resources, communications, risk, procurement, and contract management plans.
- Execution process group: Convert plans into specific actions and complete project tasks through the collaboration of the project team.
- Monitoring and Control Process Group: Monitor the progress of the project and respond to changes to ensure that the project is completed as planned.
- Close the process group: Complete the project and archive the project files.
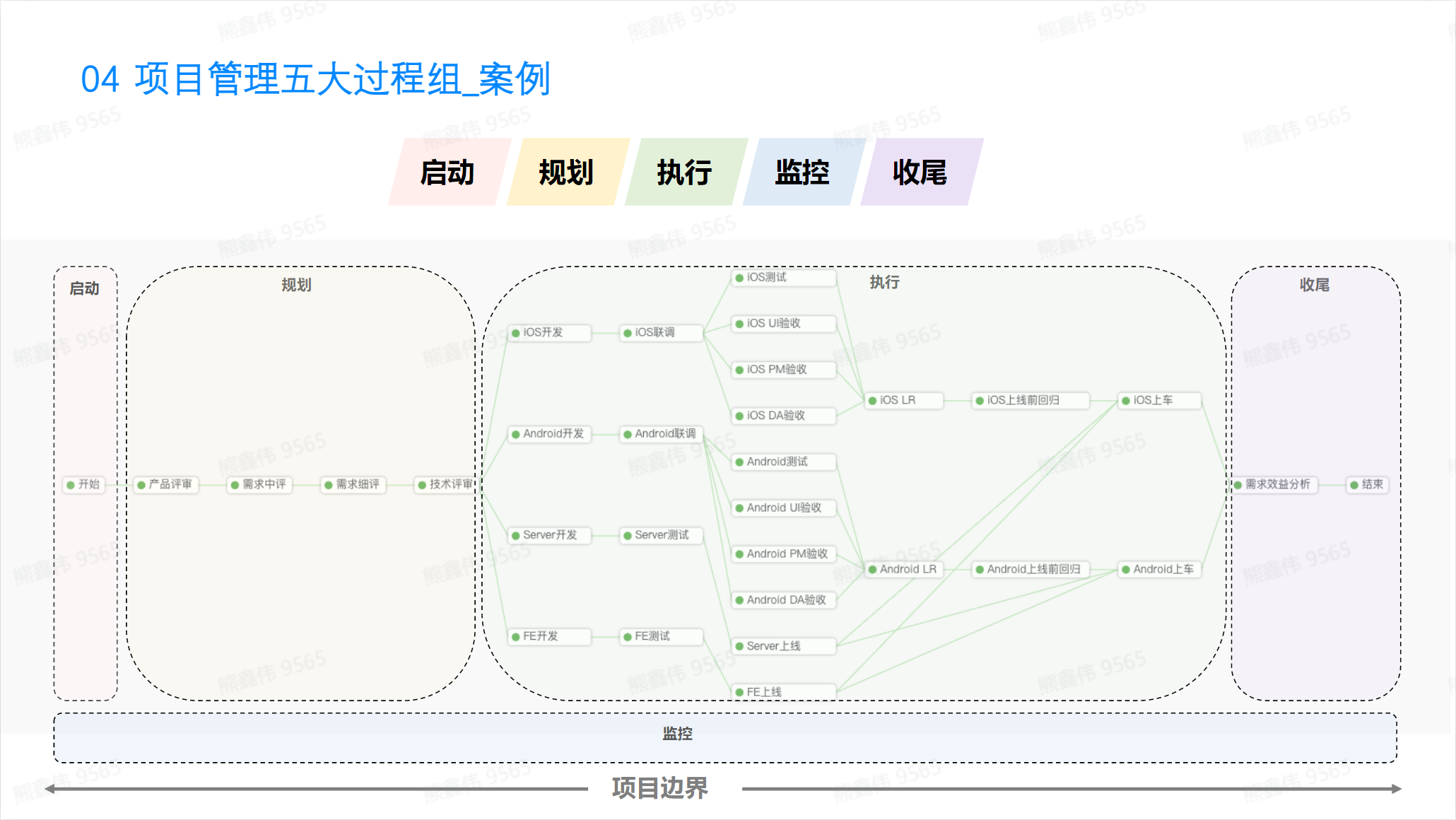
**Monitoring is responsible for the entire life cycle of product projects. **
Startup: How to start the project efficiently
Project begining
Above we have seen the five major processes of project management: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and closing. There is no doubt that the importance of how to start a project efficiently~
First take a look at a table that runs throughout:
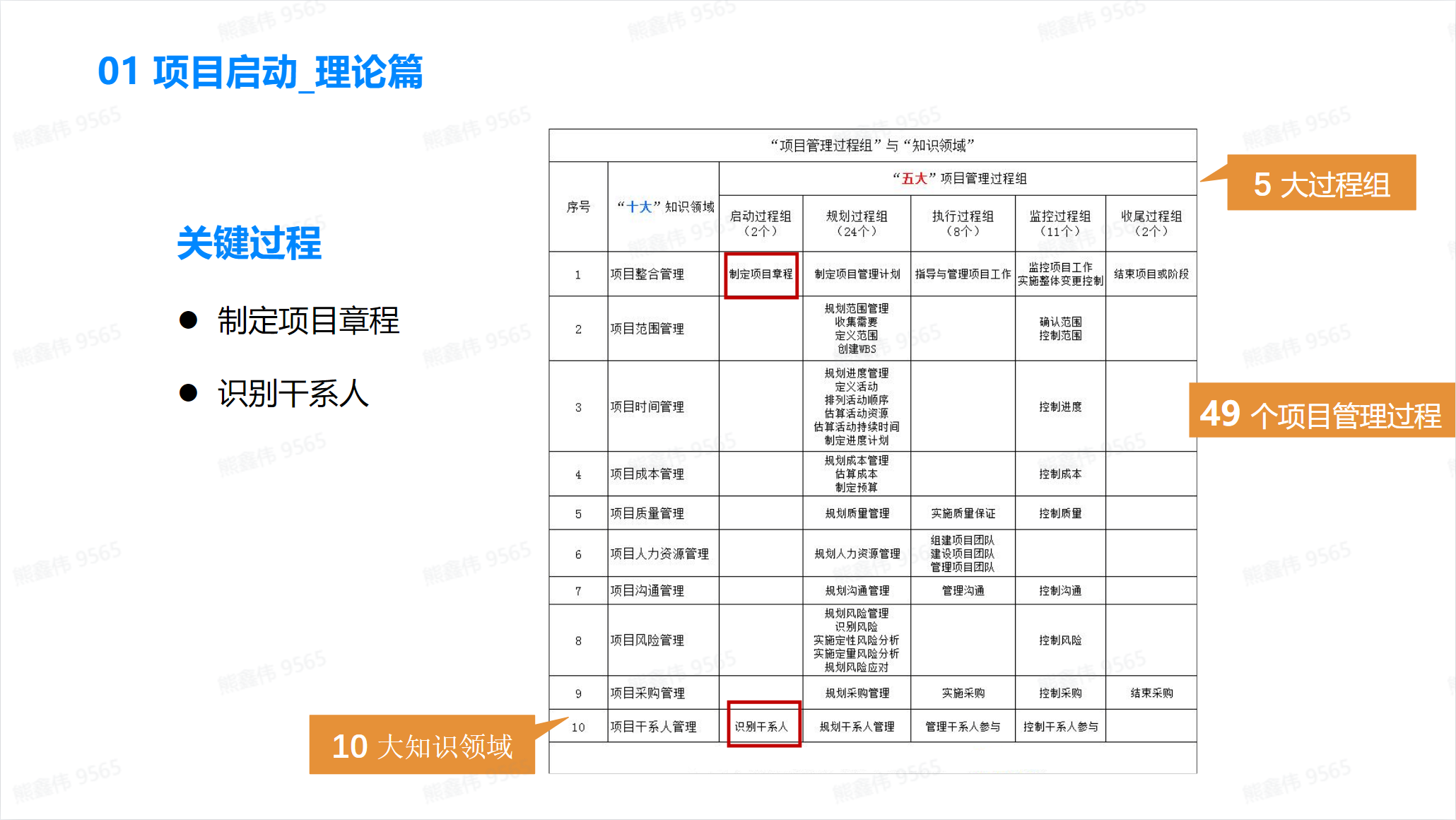
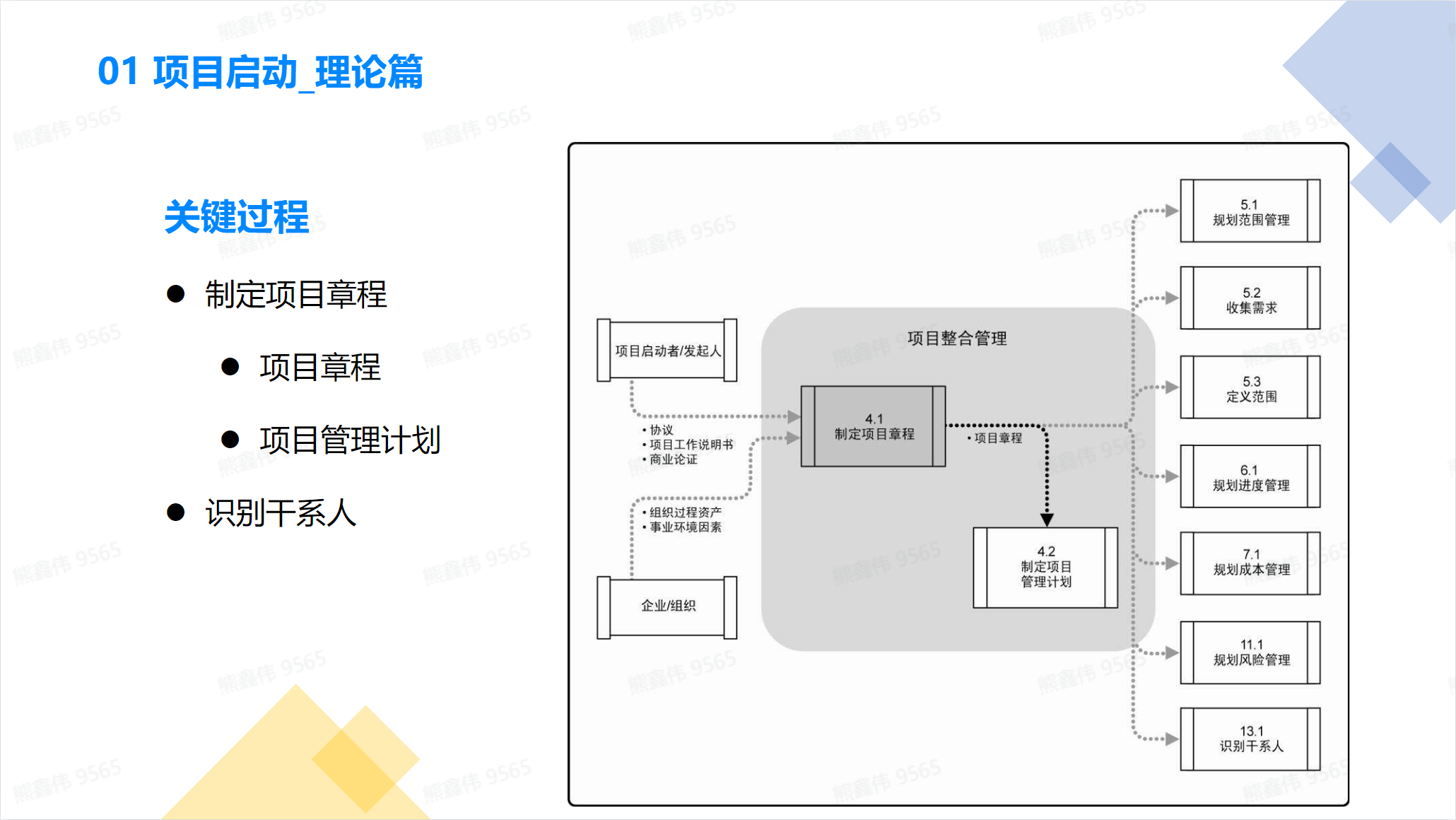
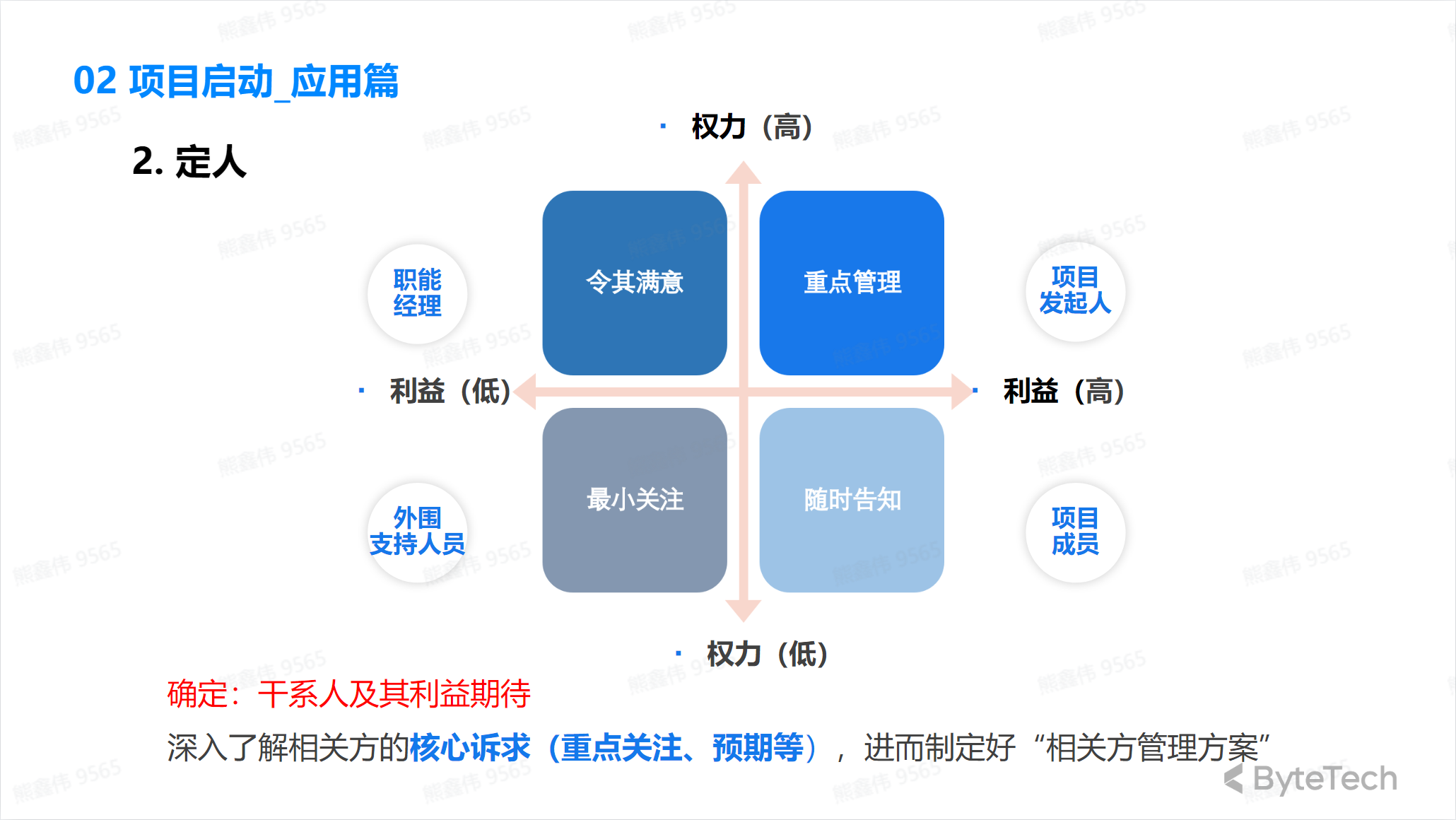
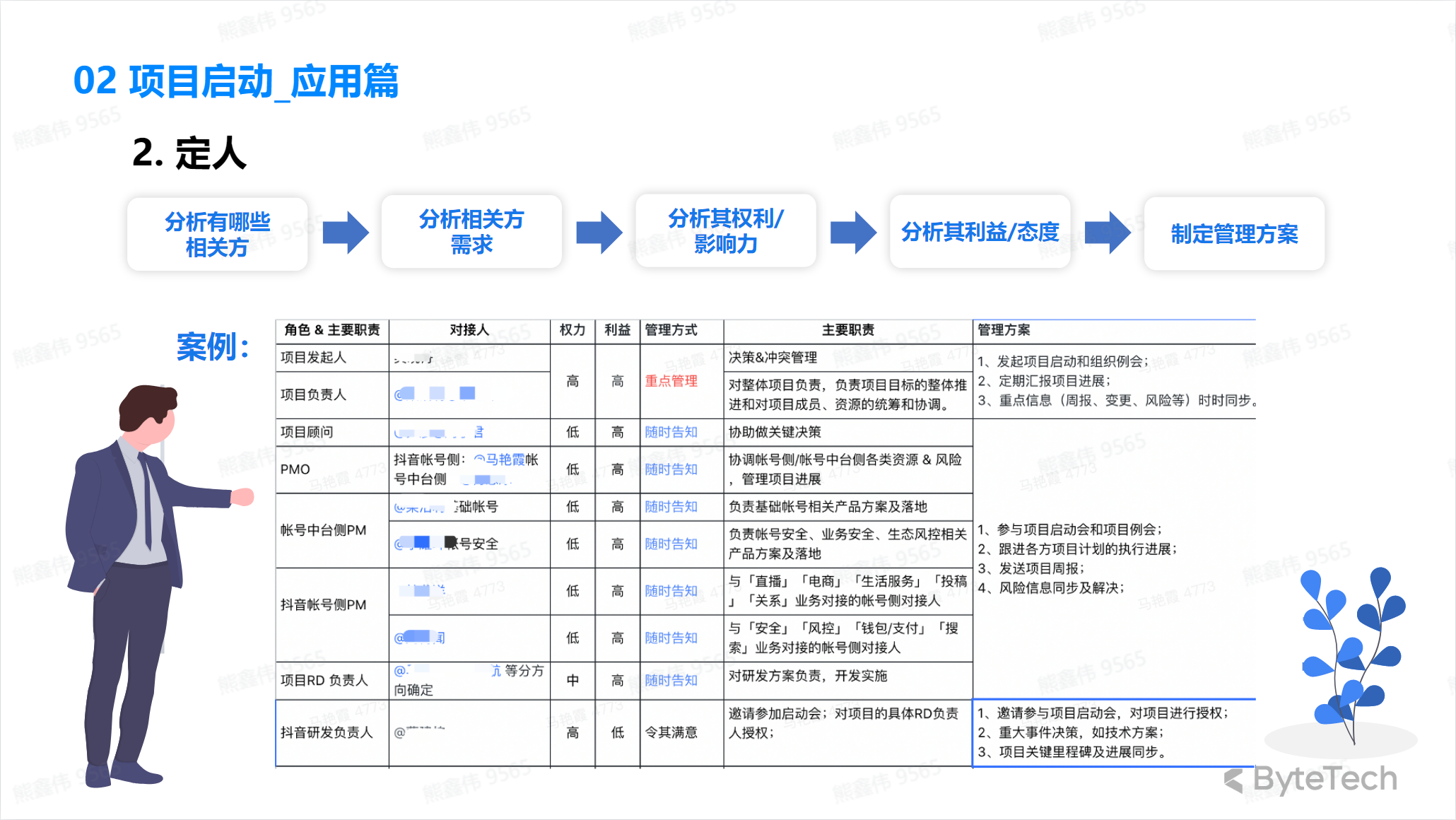
We target two key processes in the startup process:
- Develop a project charter
- Identify stakeholders
Application
⚠️Things that should be done during the project startup phase include:
Determine project goals: Clarify the purpose, scope and results of the project to ensure that the project is consistent with the strategic goals of the organization.
Form a project team: Determine the members of the project team and establish an appropriate team communication and collaboration structure.
Develop a project charter: Clarify the responsibilities and authorities of the project, and formulate a project charter to ensure orderly operation of the project.
Determine project budget: Develop a project budget based on the scope and objectives of the project, and determine the source of funding for the project.
Determine the project schedule: Develop a project schedule based on the project scope and goals, and determine project milestones.
Assess risks: Assess possible risks in the project and formulate risk response strategies.
Obtain resources: Determine the people, equipment, and materials needed for the project and acquire these resources.
Approval of startup documents: Approval and signing of project startup documents to ensure that the project has formal permission to start.
Communication plan: Develop a project communication plan to ensure that information in the project is effectively transmitted.
Contract management: Manage contracts in the project, including signing contracts, supervising contract performance and ending contracts.
Project management plan: Develop a project management plan to ensure that the project management process is orderly and efficient.
Start project execution: Start project execution according to the project management plan and project charter.
Continuously monitor the progress of the project, make adjustments and controls, and ensure that the project proceeds as planned.
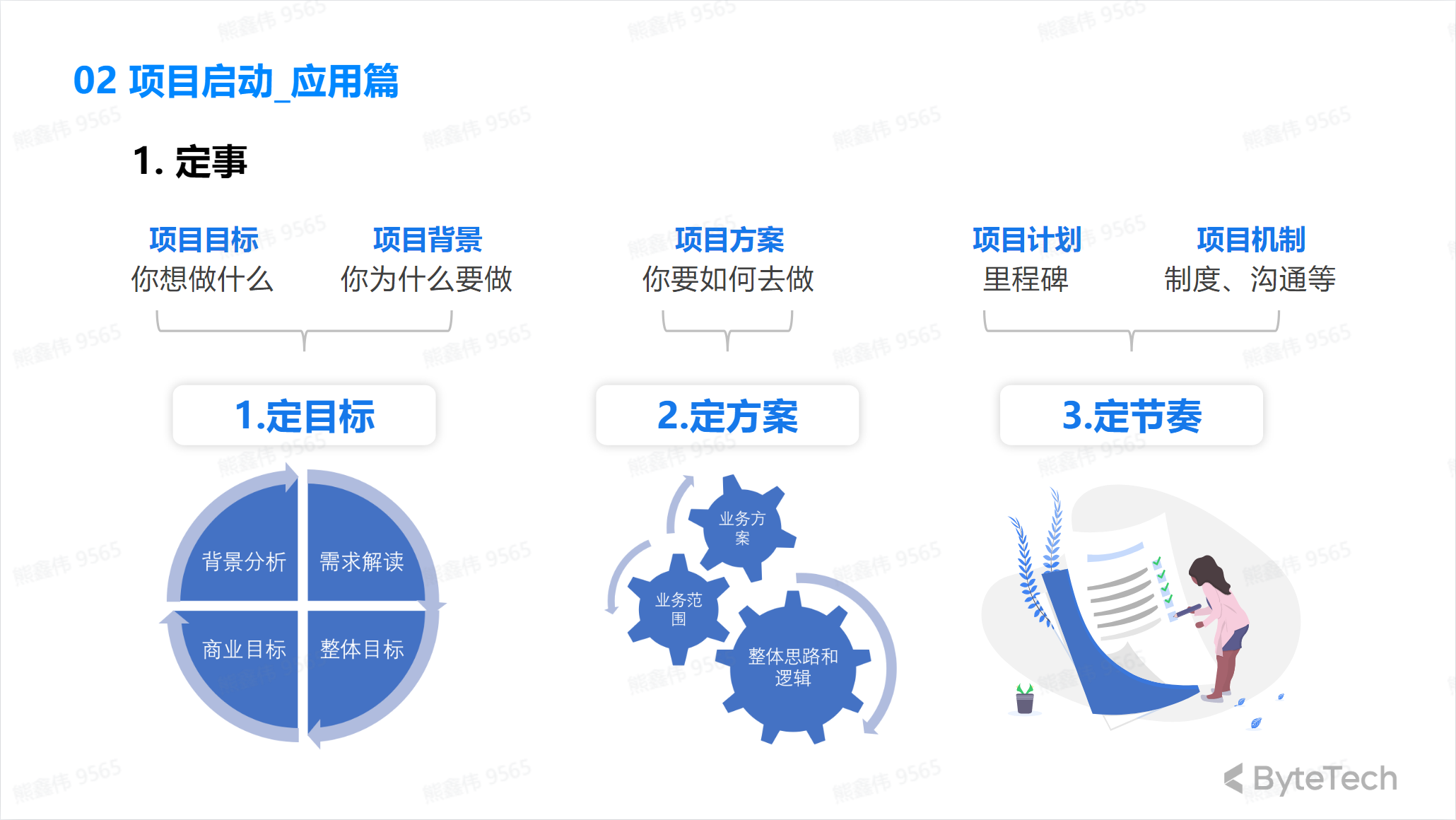
Determine the matter
💡A simple case is as follows:

Make a reservation
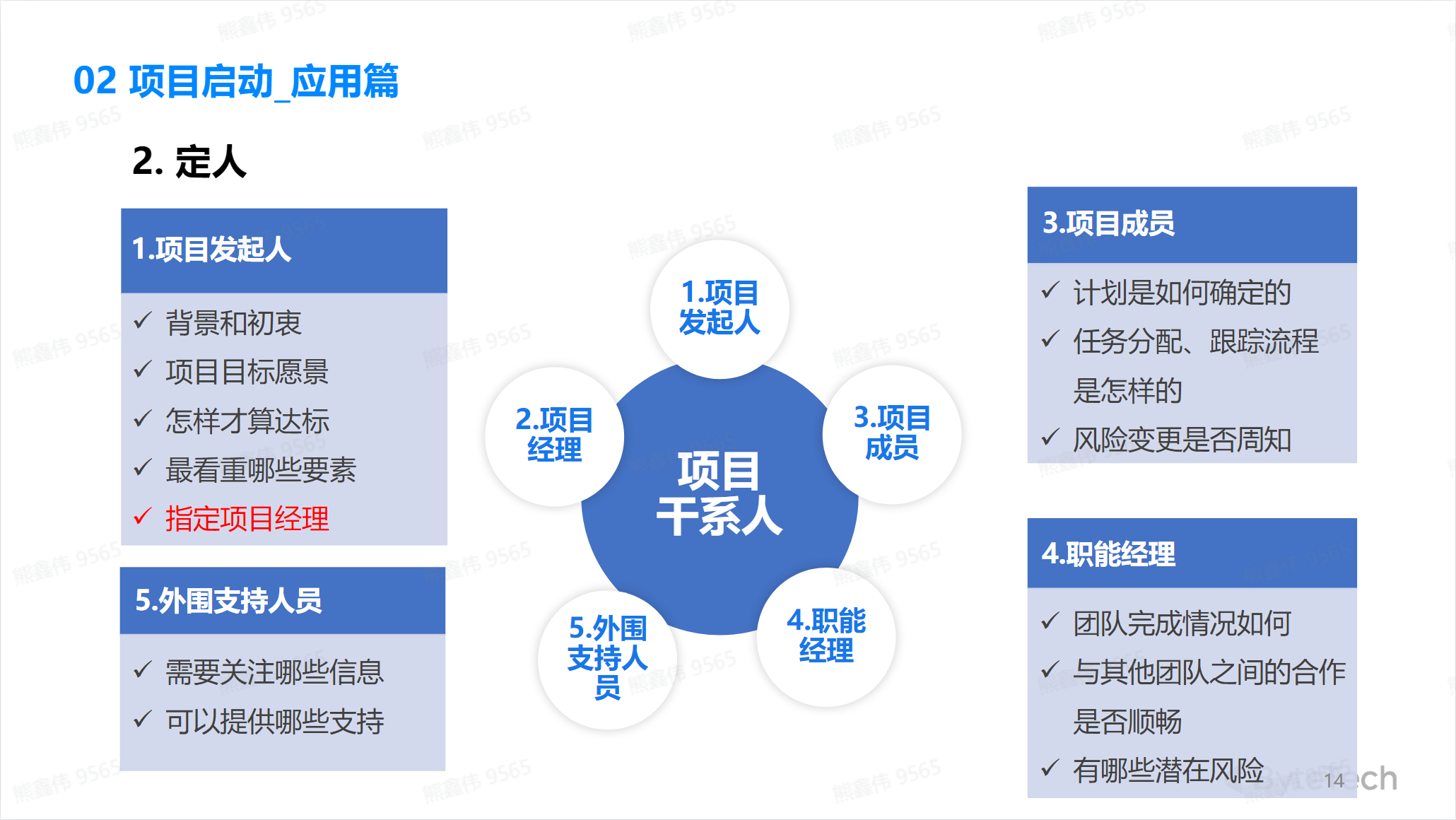
💡A simple case is as follows:
Proof of Concept (POC)
Proof of concept (English: Proof of concept, referred to as POC) is a shorter and incomplete implementation of some ideas to prove its [feasibility](https://zh.wikipedia.org/w /index.php?title=feasibility&action=edit&redlink=1), demonstrate its principle, the purpose is to verify some concepts or theories. A proof of concept is often considered a landmark implementation of a prototype.
In the project life cycle, a POC usually occurs during the planning or beginning stages of a project. During the planning stages of a project, a POC can be used to evaluate the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of a new technology to determine whether to use it in the project. If the POC results indicate that the new technology is feasible and meets project needs, then more comprehensive implementation can occur during the initial stages of the project.
A POC can help the project team determine whether the new technology meets the company’s needs and can be successful in practical applications, allowing for a better assessment of technical feasibility and cost-effectiveness during the project planning and initiation stages.
Minimalist Douyin POC proof of concept:
Demand analysis: Analyze the user needs of the minimalist version of Douyin application and determine the function and performance requirements of the application.
Technology selection: Select technologies suitable for application development, such as languages, frameworks, etc.
Develop a prototype: Develop a prototype of the application based on demand analysis and technology selection, and determine the application interface and interaction method.
Build POC: Develop POC based on the prototype to ensure that the application can meet user needs and performance requirements.
Test verification: Test the POC to verify whether the function and performance of the application meet the requirements.
Evaluate the results: Evaluate the results of the POC to determine whether to continue developing the application.
Documentation: Record the process and results of the POC for future reference.
Optimize the plan: If the POC results are feasible, formulate a plan to improve the application and determine the actual development tasks and progress.
Execution plan: Execute the project according to the plan, using the results of the POC as a basis.
Continuous monitoring and management: Continuously monitor and manage the progress and quality of the project during the project implementation process, and adjust and control the project in a timely manner.
Project closure: Complete the project and archive the project files.
Feedback and improvement: Improve the project based on the feedback results after the project is completed, and record it for future reference.
Planning: How to formulate project planning
Project planning is an important part of project management and is the key to project success. Developing a project plan requires following these steps:
- Clarify project goals: First, you need to clarify the goals and success criteria of the project and translate them into specific project goals.
- Analyze project requirements: Determine the tasks and deliverables that need to be completed by communicating and negotiating with relevant personnel.
- Develop project plan: Based on project goals and needs, develop project plan, including project schedule, cost, resources and risk management, etc.
- Develop project documents: According to the project plan, develop project documents, such as project charter, instructions, project management plan, etc.
- Execute project plan: Execute the project according to the project plan and documents, and continuously monitor project progress and performance.
- Update the project plan: As the project progresses, the project plan may need to be updated and adjusted.
- Risk management: During the project process, project risks need to be identified, assessed and responded to. This includes identifying various possible risks faced by the project, assessing the impact of the risks, formulating risk response strategies and implementing risk response measures.
- Communication management: Project communication management is one of the important links in project management. During the project process, an effective communication mechanism needs to be established to ensure information communication and coordination among project-related personnel.
- Monitoring and Control: Monitor and control the project in accordance with the project plan and documents. Including monitoring and controlling project progress, quality, costs, risks, etc.
- Project end: When the project is completed, a project end inspection needs to be carried out to evaluate the project and summarize the project. This will help improve the efficiency and quality of future project management.
Planning Management

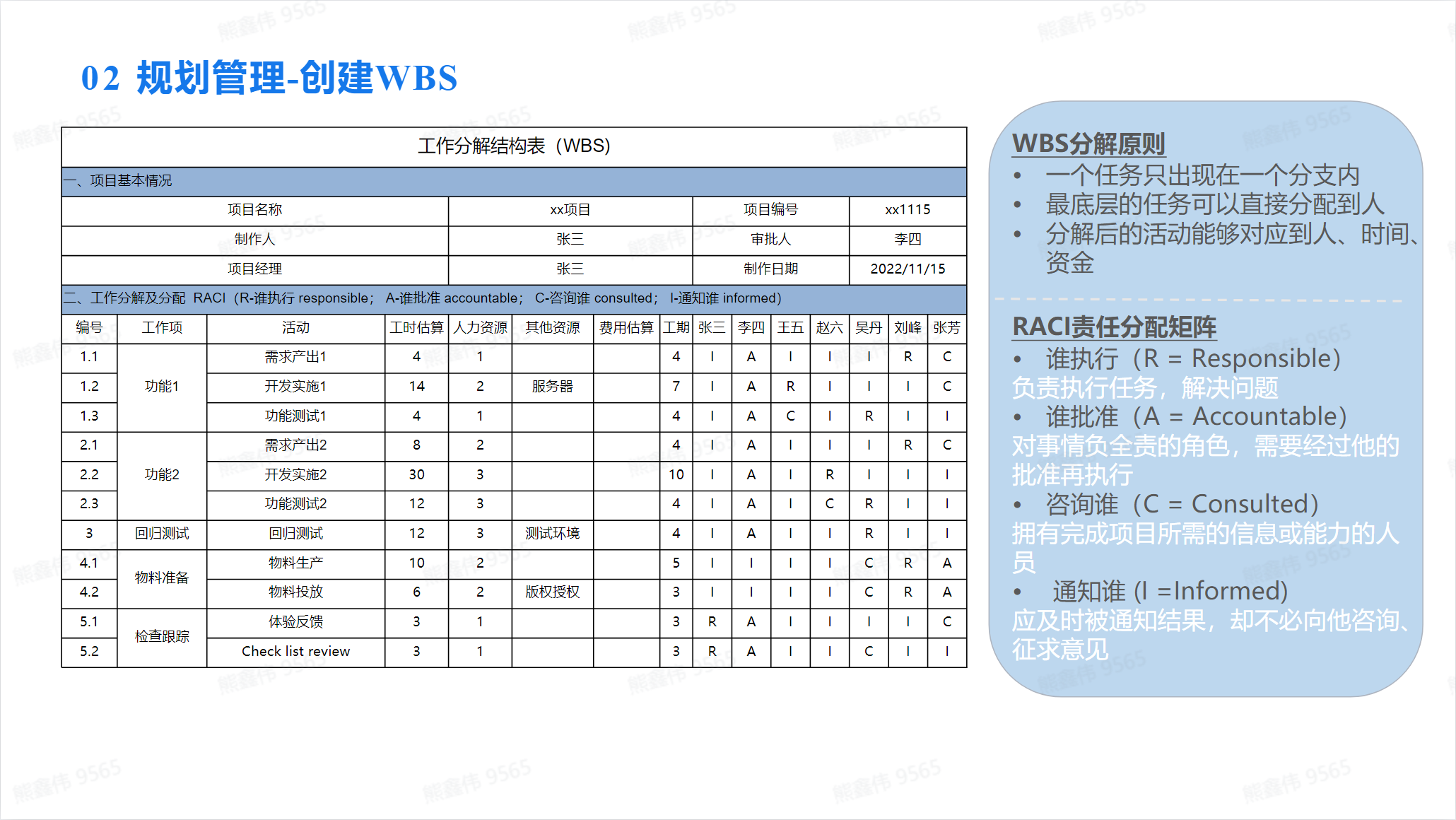
Create WBS
WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) means work breakdown structure. It is a tool for organizing and managing project tasks, helping project organizers better control the progress and quality of the project by dividing the overall goal of the project into smaller, manageable parts.
The WBS is usually organized in the form of a tree structure, with the overall goal of the project at the top, and the subtasks decomposed below, and so on. The tasks at each level are subdivisions of the tasks at the previous level. The purpose of this is to ensure that each sub-task can be completed independently, and also to track the overall progress of the project.
WBS can help project organizers better understand the scope, schedule and risks of the project, and can be used to determine the project’s resource requirements and schedule tasks.
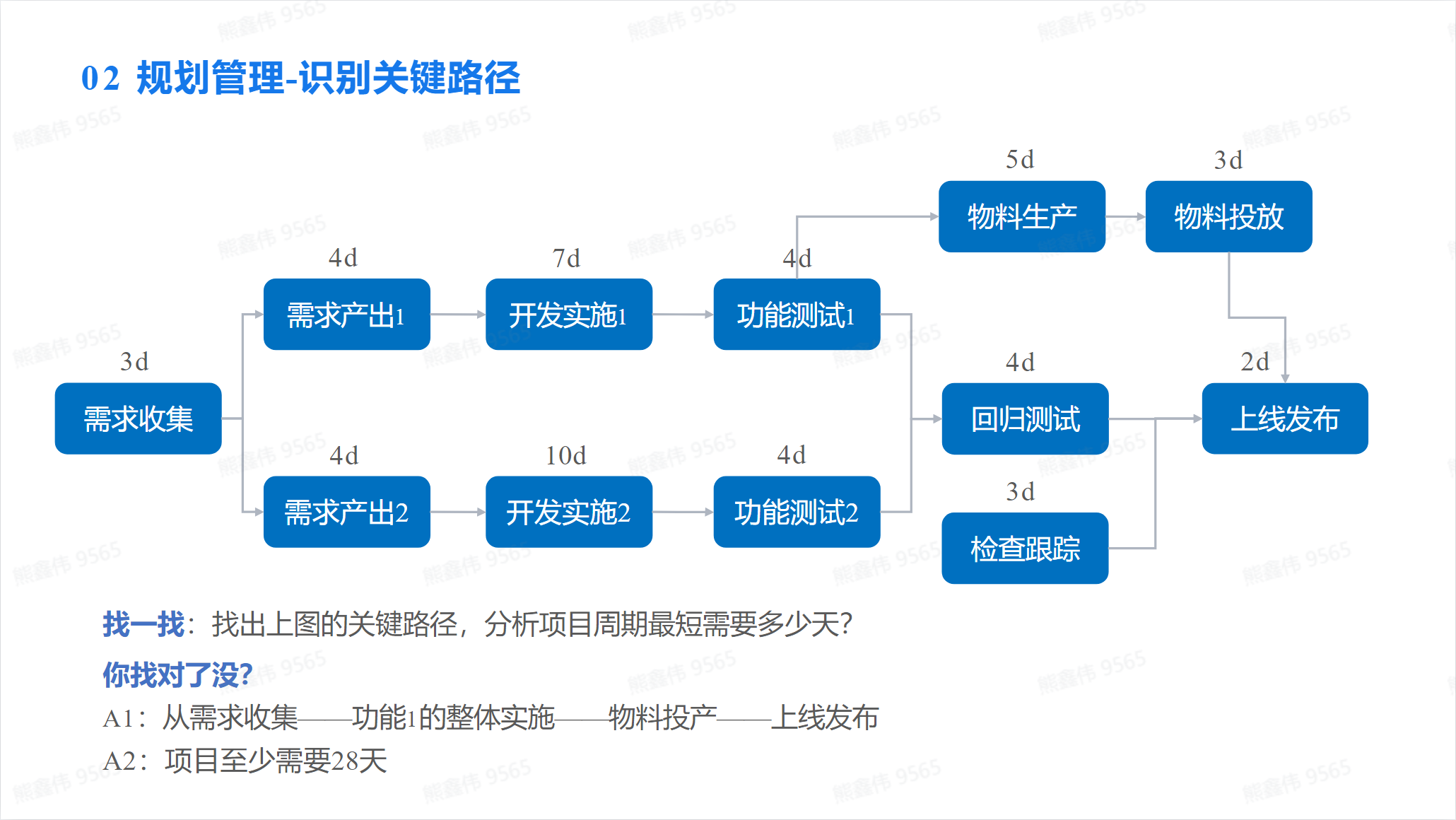
Planning Management Chart
The project planning chart can calculate the project development cycle, which is clear at a glance~
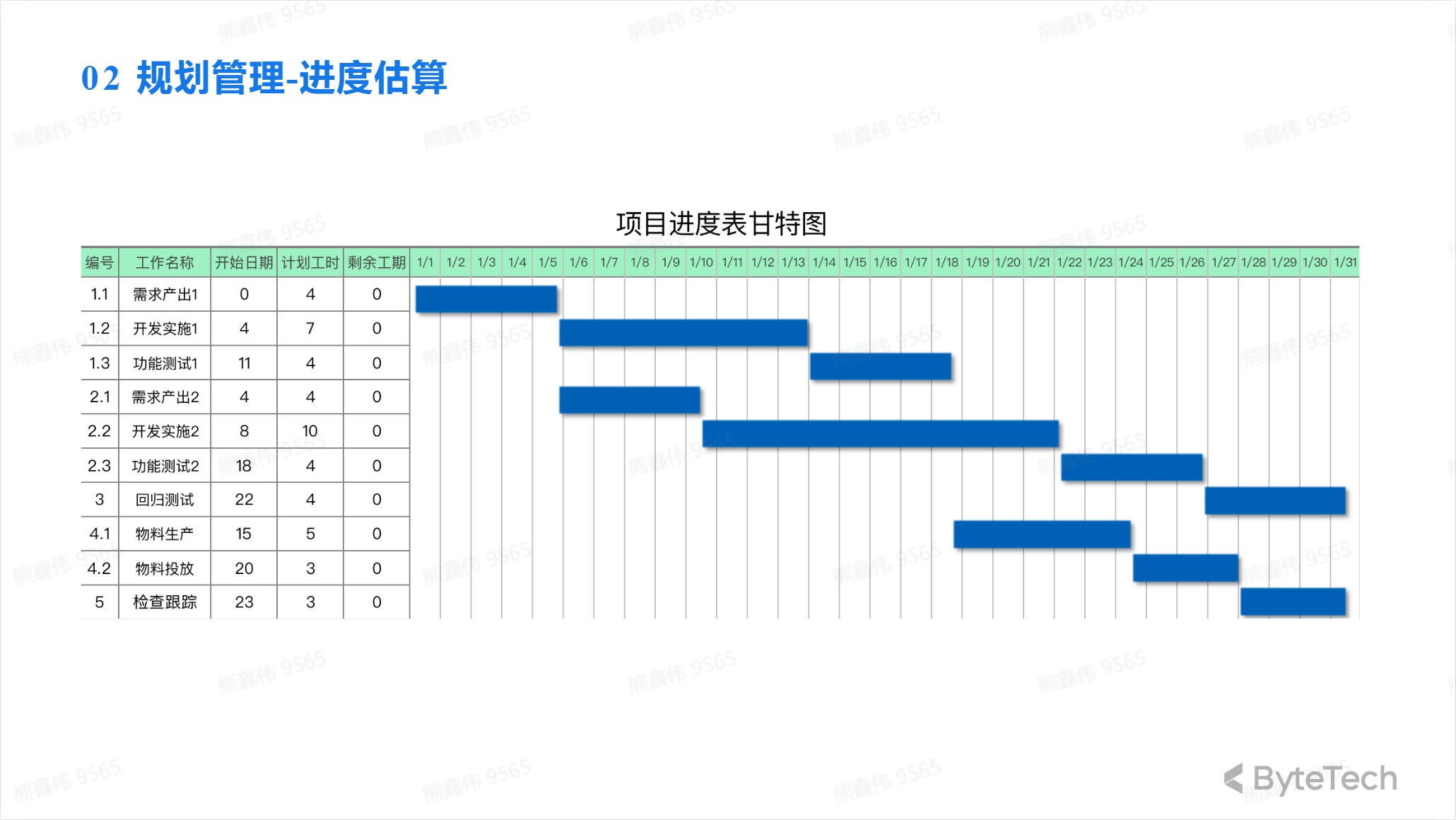
Gantt chart
Gantt chart is a project management tool used to represent the progress and resource allocation of a project. It is a graphical tool that usually consists of a horizontal timeline and a vertical task bar.
On a Gantt chart, each task corresponds to a horizontal bar indicating the task’s start time and end time. By looking at the Gantt chart, you can easily understand the progress of the project, the dependencies between tasks, and resource allocation.
Gantt charts can help project organizers better grasp project progress, adjust project plans, and better control project progress and resource allocation. At the same time, it also allows other members of the project to better understand the progress of the project.
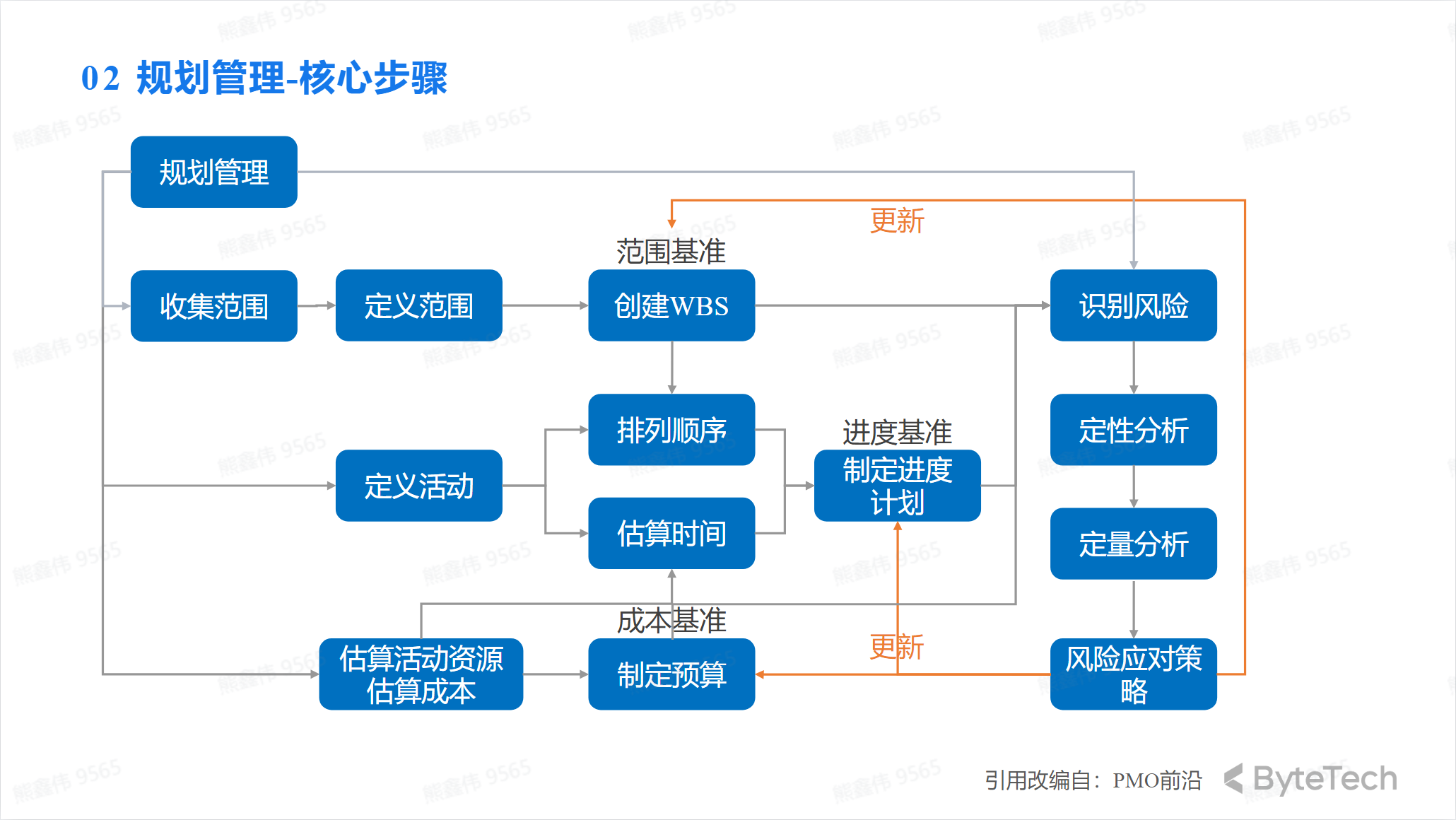
Core steps
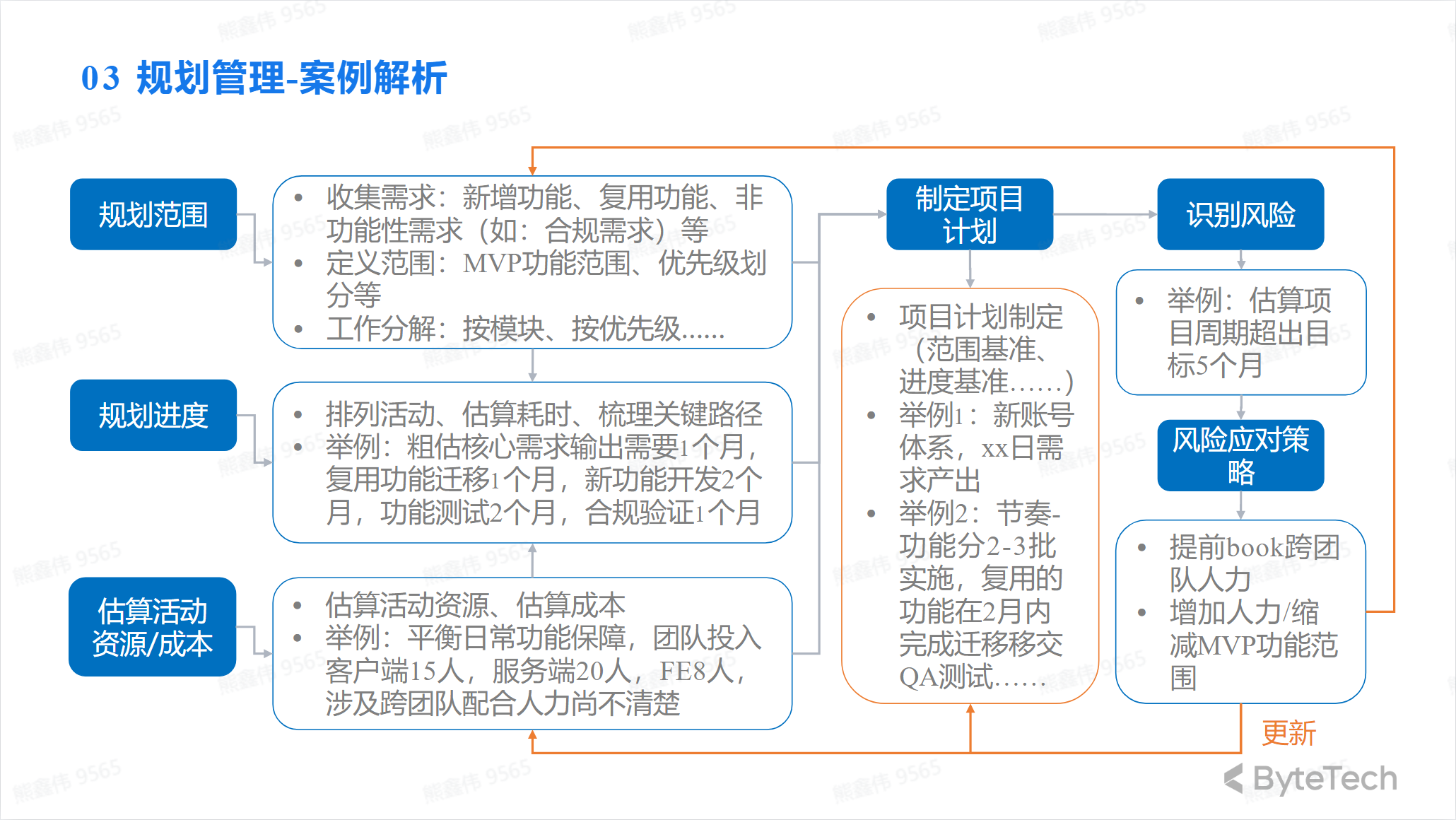
Planning Management-Case Analysis
[[MVP version]]:
The concept of MVP is a concept proposed by Eric Ries in “Lean Startup”. Simply put, it means that the development team obtains user feedback by providing a minimum viable product, and continues to iterate rapidly on this minimum viable product until the product reaches a relatively stable stage. . MVP is very important for entrepreneurial teams, as it can quickly verify the team’s goals and enable rapid trial and error.
Project background: With the company’s strategic development needs, business A must initiate key projects
Project content: Based on the existing capabilities of xx company, a new APP is developed and released in a new national market.
Project Goal: Complete MVP version APP development in 5 months
Some nouns:
- Self-test[[case]] (Self-Testing Case) refers to the test cases developed and executed by the developers themselves during the software development process.
- Self-test case is a very important quality assurance method, which can help developers discover and repair errors and defects in software earlier. Self-test cases usually include functional testing, performance testing, reliability testing and compatibility testing.
- Self-test cases can help developers ensure the quality and reliability of software, improve software development efficiency and reduce software maintenance costs. It can also help ensure that the software meets user needs before release.
- [[QA]] refers to Quality Assurance, which is a systematic, preventive process designed to ensure that a product or service meets quality standards.
- The purpose of QA is to ensure that a product or service reaches the expected level of quality through specifications, procedures, standards and testing. The QA process includes quality planning, quality control, quality assurance and quality improvement.
- The QA process can help companies or organizations improve the quality of products and services, meet customer needs, and improve market competitiveness and brand image. QA can also help companies or organizations reduce the cost of production and service of defective products, improve production efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- [[RD]] refers to Research and Development, that is, research and development. R&D refers to the research and development of products, services, technologies, etc. by enterprises or organizations to improve their competitiveness and innovation capabilities. Research and development includes new product research and development, technology improvement, new process development, etc.
- R&D can help enterprises or organizations launch new products and services, improve product quality and performance, meet market demand and increase market share, improve production efficiency and reduce production costs, and improve technological levels and competitiveness. Research and development is also an important investment for a business or organization because it can bring long-term economic benefits.
- [[Review]] refers to a code review or code review. It is an important means of quality assurance and improvement, aiming to discover and correct errors, defects, and potential problems in the code through the review and evaluation of the code by others
- Code review can help ensure code quality, improve code readability, maintainability and scalability, and reduce software maintenance costs and risks.
- Generally speaking, code reviews can be done by humans or tools. Human reviews are usually done by one or more developers, while tool reviews are done using automated tools that can scan the code and find potential problems.
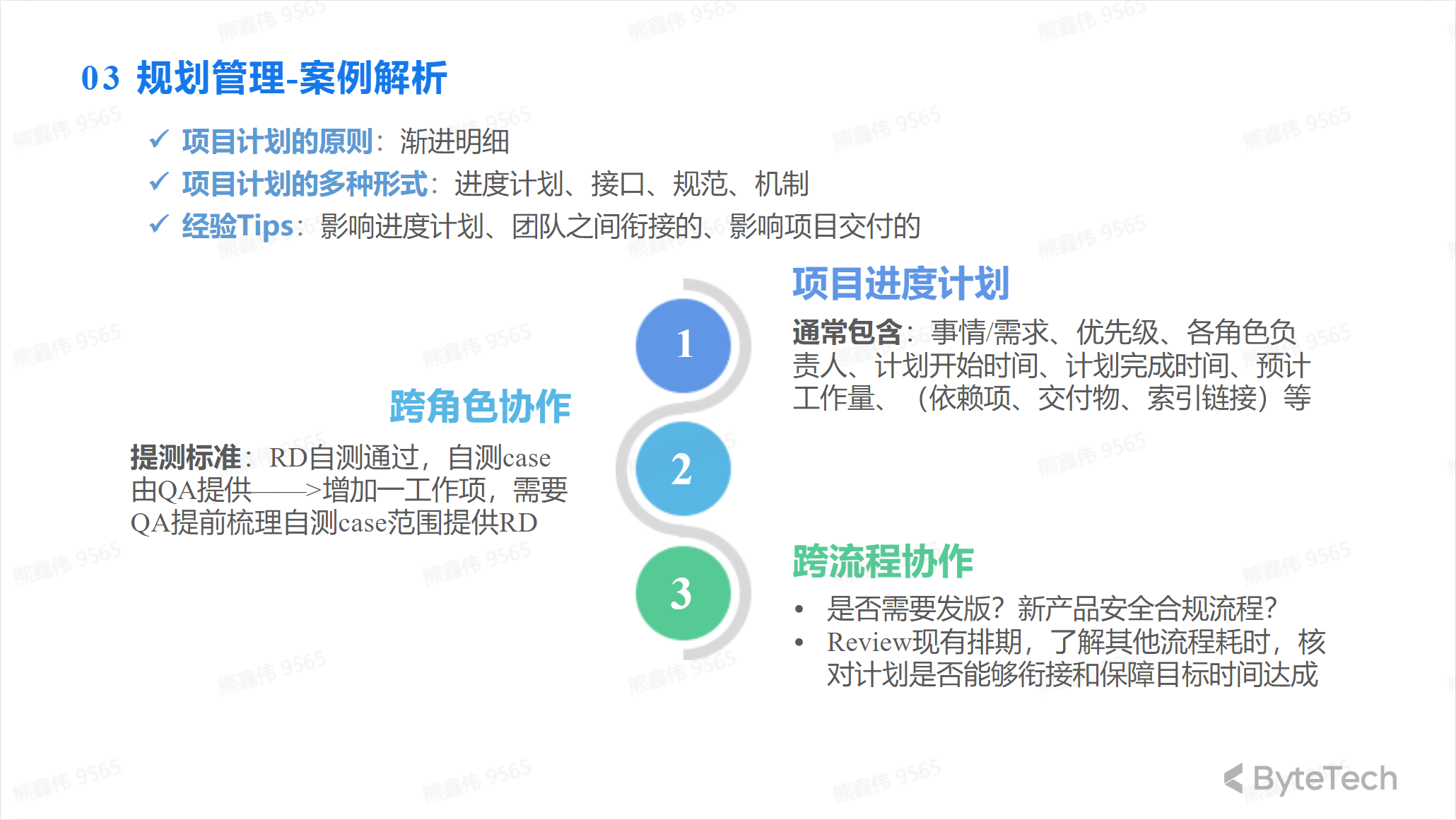
Experience summary

Execution: How to follow up efficiently
When you need to ensure efficient follow-up, pay attention to the following aspects:
- Establish clear goals and plans: First, you need to establish the goals and plans of the project, and ensure that all relevant personnel understand and work according to these goals and plans.
- Establish an effective communication mechanism: By establishing an effective communication mechanism, ensure information communication and coordination among project-related personnel, and identify and solve problems in a timely manner.
- Regular follow-up and reporting: Establish a regular follow-up and reporting mechanism to monitor and control project progress, quality, costs, risks, etc.
- Agile Management: By using agile management methods, you can react more quickly and be able to cope with changes that occur in the project.
- Organize team training: Hold regular team training to help team members improve their skills and knowledge, and improve teamwork and collaboration capabilities.
- Overall consideration: Overall consideration of all relevant factors in the project, including personnel, funds, technology, etc., to ensure that the project can be successfully completed.
Conference system promotion and implementation

**Meeting time is very important, don’t waste other people’s time, there is no need to hold a group meeting if it can be solved in an individual meeting. **
Specify template and plan before meeting:
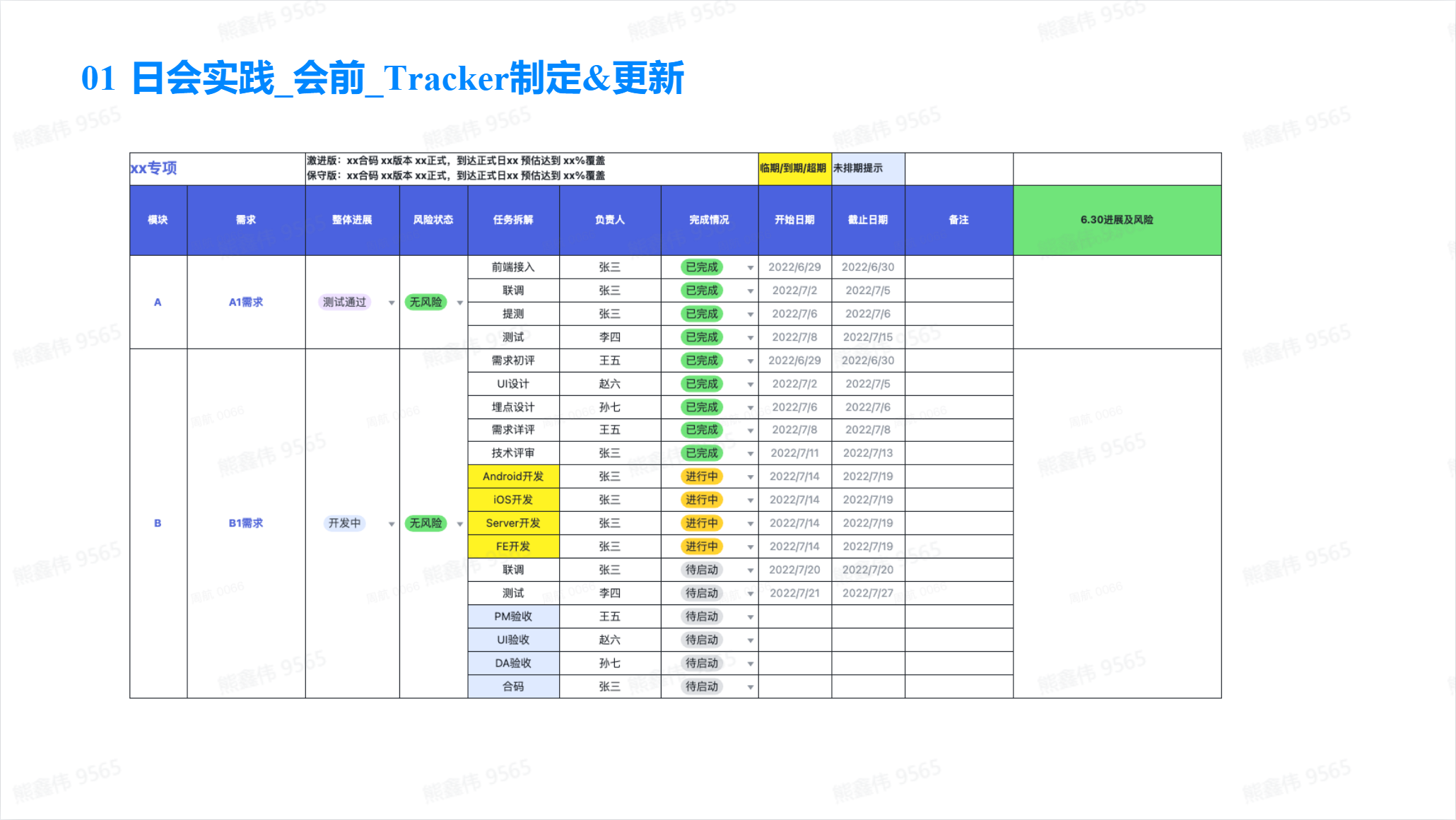
Four steps for progress confirmation
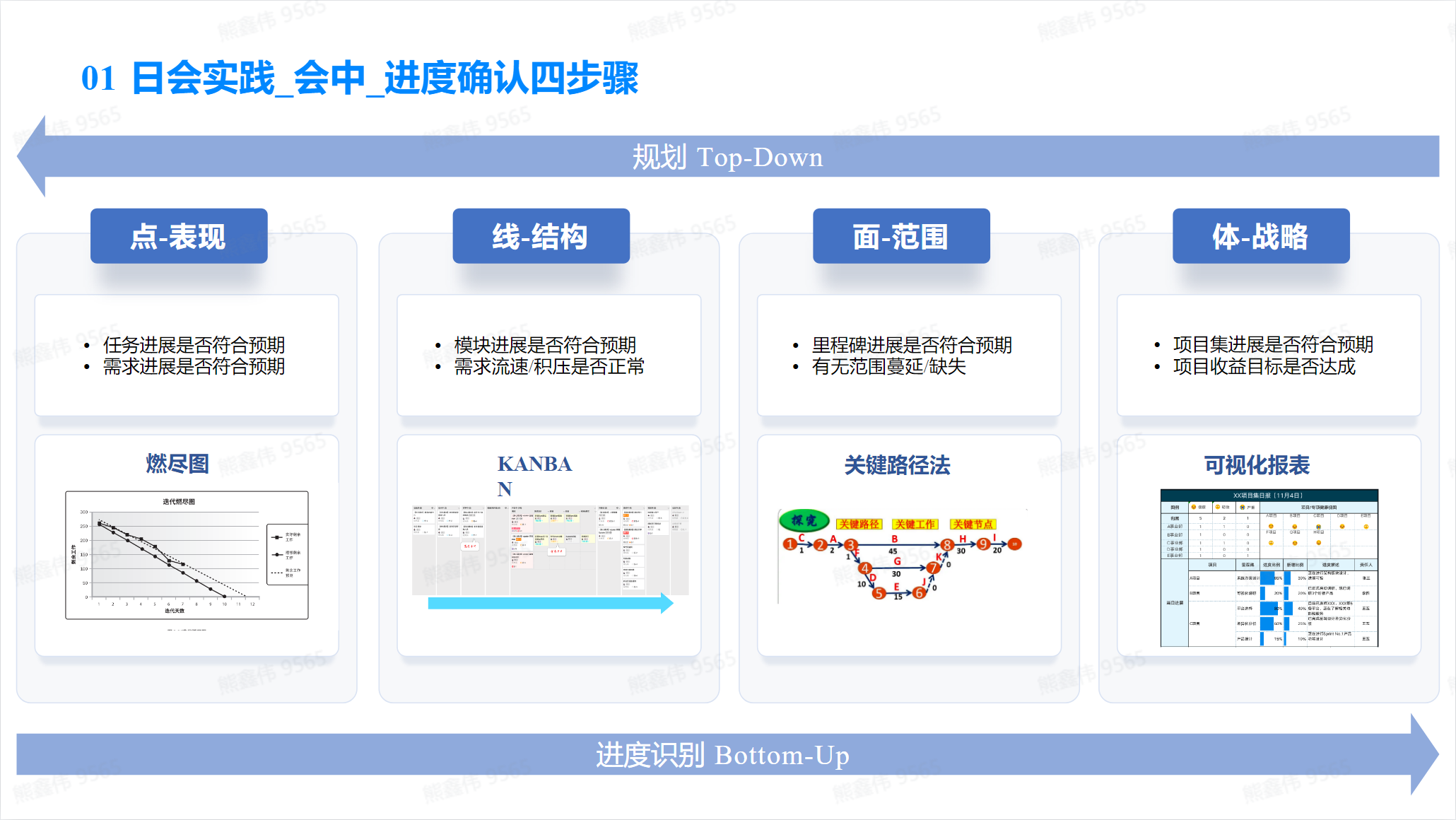
Effective guidance in meetings
**In the open source community, I often see two methods of meeting guidance. One is the issue and solution of the specified meeting in GitHub Dicussions. The second is to collaboratively write meeting summaries and plans in Google Docs, nothon or Feishu documents. **
We should note:
- Clear topic: Before the meeting, determine the topic and purpose of the meeting and ensure that all participants understand it.
- Be well prepared: During the meeting, prepare meeting materials and documents in advance to provide participants with useful information.
- Control time: Strictly control meeting time and ensure that the meeting ends within the specified time.
- Guide the discussion: Guide the discussion through questions and exercises, allowing participants to express their opinions and solve problems.
- Provide feedback: Provide regular feedback to ensure the goals and plans of the meeting are being achieved.
- Document Decisions: Document the decisions and action plans made during the meeting to ensure that all participants understand and follow them.
- Increase participation: Increase participant participation by asking questions, providing opportunities to speak, and encouraging participation.

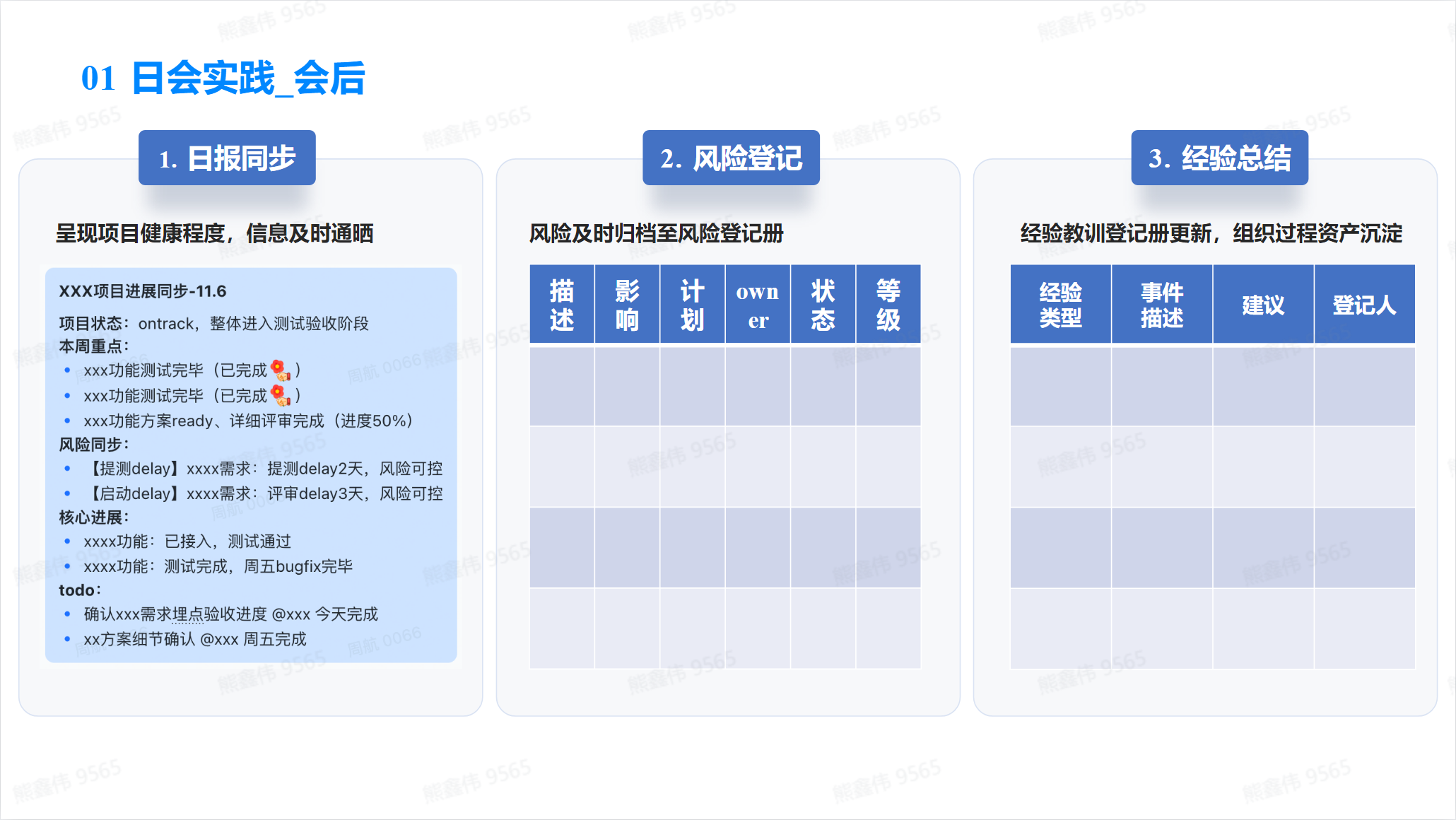
After the meeting
After the meeting, meeting minutes need to be sent, including:
- Meeting Topic: Outline the main topics and purpose of the meeting.
- Meeting Minutes: Record in detail the discussions and decisions made during the meeting.
- Action plan: List the action plan and next steps reached during the meeting.
- Deadline: Set a deadline for completion of the action plan.
- Responsible person: Assign a responsible person to be responsible for completing the action plan.
- Follow-up: Designate a responsible person to follow up on the execution of the action plan.
**🔍 The following is a meeting minutes template: **
Conference theme: [Conference theme]
Meeting date: [meeting date]
Meeting place: [meeting place]
Participants: [List of participants]
Meeting agenda:
- [Issue 1]
- [Issue 2]
- [Issue 3]
Meeting minutes:
[Issue 1]
- [Discussion results]
- [Decision]
[Issue 2]
- [Discussion results]
- [Decision]
[Issue 3]
- [Discussion results]
- [Decision]
action plan:
- [Task 1]
- [Detailed description]
- [Responsible person]
- [deadline]
- [Task 2]
- [Detailed description]
- [Responsible person]
- [deadline]
- [Task 3]
- [Detailed description]
- [Responsible Person]
- [deadline]
The next step of the job:
- [Job 1]
- [Job 2]
- [Job 3]
Meeting end time: [meeting end time]
Next meeting time: [next meeting time]
Minute writer: [Minute writer]
Contact information: [Contact information]
Please complete the [Action Plan] by [Deadline] and report on progress at the next meeting.
Meeting minutes should be sent to all participants as soon as possible after the meeting so that they can understand the progress and results of the meeting and ensure that they have completed their work according to the requirements of the action plan.
In addition, before the next meeting, ensure that all action plans are completed and reported during the meeting. If there are any problems or delays, they should be reported to the project manager as early as possible.
Rhythm Alignment
[[OKR]]:
OKR (Objectives and Key Results) is an objective management method, a process in an organization to define goals and indicators and achieve them.
It consists of two parts:
- Objectives: Objectives are the results that the organization wants to achieve. It should be clear, specific, measurable, and challenging.
- Key Results: Key results are the specific indicators that need to be achieved to achieve the goal. It should be measurable and can be tracked and evaluated in some way.
The purpose of OKR is to help organizations better manage goals and results and achieve goals through continuous tracking and evaluation. OKR can help organizations better manage goals and results, better control project progress, and better evaluate project effectiveness. The OKR method is often used for enterprise-level goal management and is implemented differently in different companies and organizations.
The advantage of OKR is that it helps organizations better position and track goals and better evaluate project effectiveness. The OKR approach also helps organizations communicate and coordinate better, and can improve project team motivation and performance.
However, if OKRs are not implemented carefully or properly supported, it can lead to project deviation or failure. Therefore, when implementing OKR, you need to ensure that there is a good management team to organize and supervise the implementation process to ensure that all goals and key results are reasonable and can be effectively tracked and evaluated. In addition, it is also necessary to ensure that all employees and teams can understand and support the goals and methods of OKR to ensure that OKR can be effectively implemented.

Gentleman’s Agreement
“Gentleman’s Agreement” refers to the rules and guidelines agreed between project participants in project management. These rules and guidelines can help ensure that the project runs smoothly and that communication and collaboration between project members are effective.
A gentleman’s agreement may include the following:
- Project goals and expected results
- Project Progress and Progress Reports
- Assignment of tasks and responsibilities
- Risk management and problem resolution
- Communications plan and communication channels
- Code of conduct among project members
It is important to ensure that all project members follow gentleman’s agreements and that these agreements are valid and can help the project be completed smoothly.
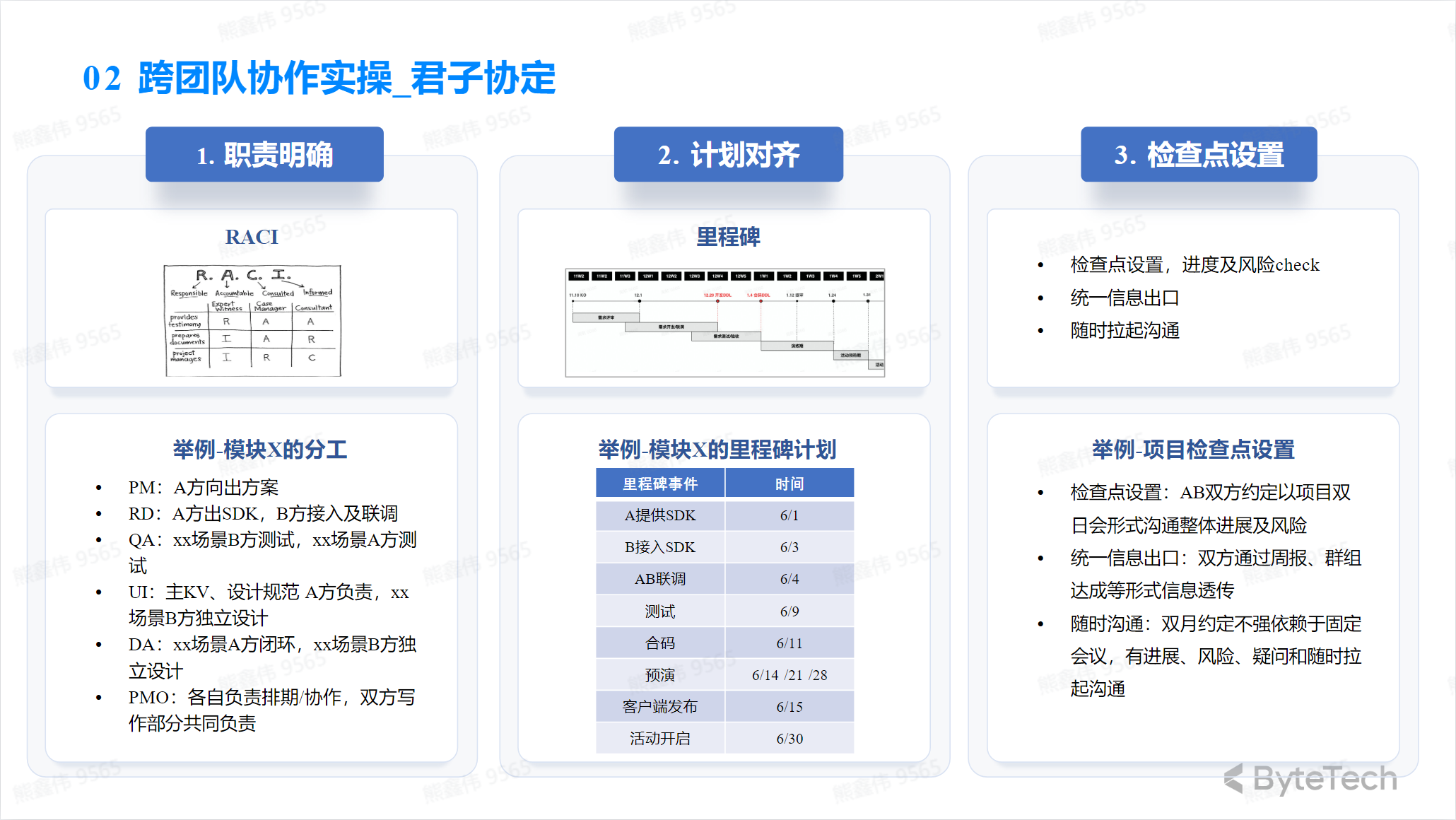
Collaborate across teams to solve problems

Open borders:

Execution: How to embrace change
🎈 **What never changes is change itself. Face changes squarely and face them with a positive attitude. **
The execution phase in project management refers to the process of converting project plans into actual actions. During this phase, the project manager needs to ensure that the project team executes the project plan correctly and manages the project’s schedule and progress.
Embracing change is very important during the execution phase, as the progress of the project is often affected by various factors, causing changes to the plan.
To embrace change, project managers can take the following steps:
- Establish a flexible plan: The project manager should establish a flexible plan rather than a fixed plan so that it can cope with changes.
- Establish a risk management plan: The project manager should evaluate the risks that may arise in the project and establish an effective risk management plan.
- Frequently monitor project progress: Project managers should frequently monitor project progress, identify problems in a timely manner and take measures.
- Maintain open communication: The project manager should maintain open communication so that the project team and other relevant personnel can participate in the project.
- Quick response: Project managers should be able to react and take action quickly to deal with changes.
Through these steps, the project manager can help the project team better adapt to changes and enable the project to be successfully completed.
In addition, project managers should also cultivate flexibility and adaptability among team members. This can be done by providing training and support within the project to help team members learn to cope with change and find opportunities in change.
All in all, embracing change is a very important point in project management. Project managers need to take effective steps to deal with changes and help the project be successfully completed.
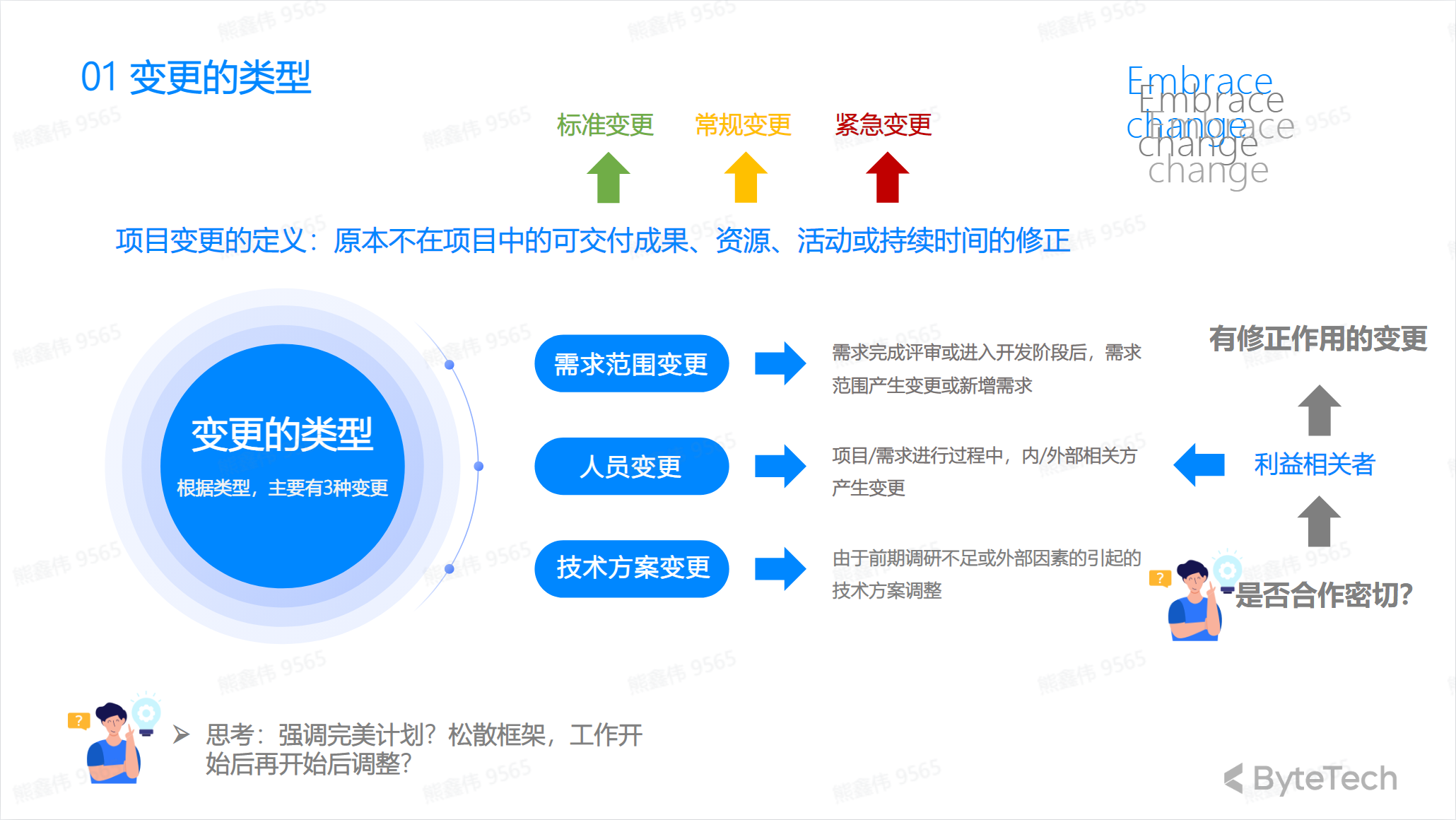
Type of change
Common types of changes include:
- Scope changes: modifications to the project scope, including adding or deleting project tasks.
- Time changes: modifications to the project schedule, including adjustments to the project start and end time.
- Cost changes: modifications to the project budget, including increases or decreases in project costs.
- Quality changes: modifications to project quality standards.
- Personnel changes: modifications to project team members, including adding or deleting team members.
- Communication changes: Modifications to the project communication plan.
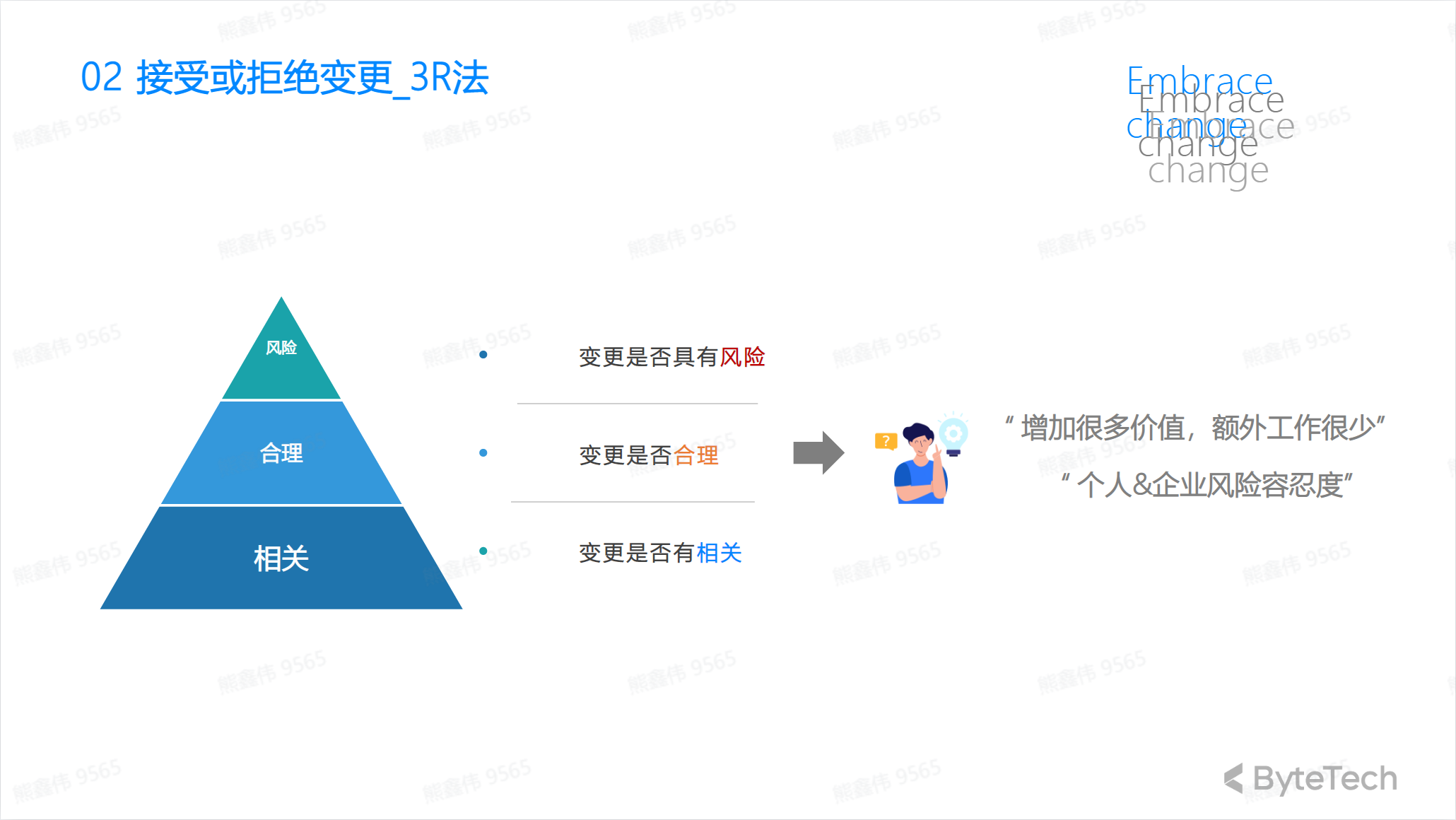
Accept or reject change methods
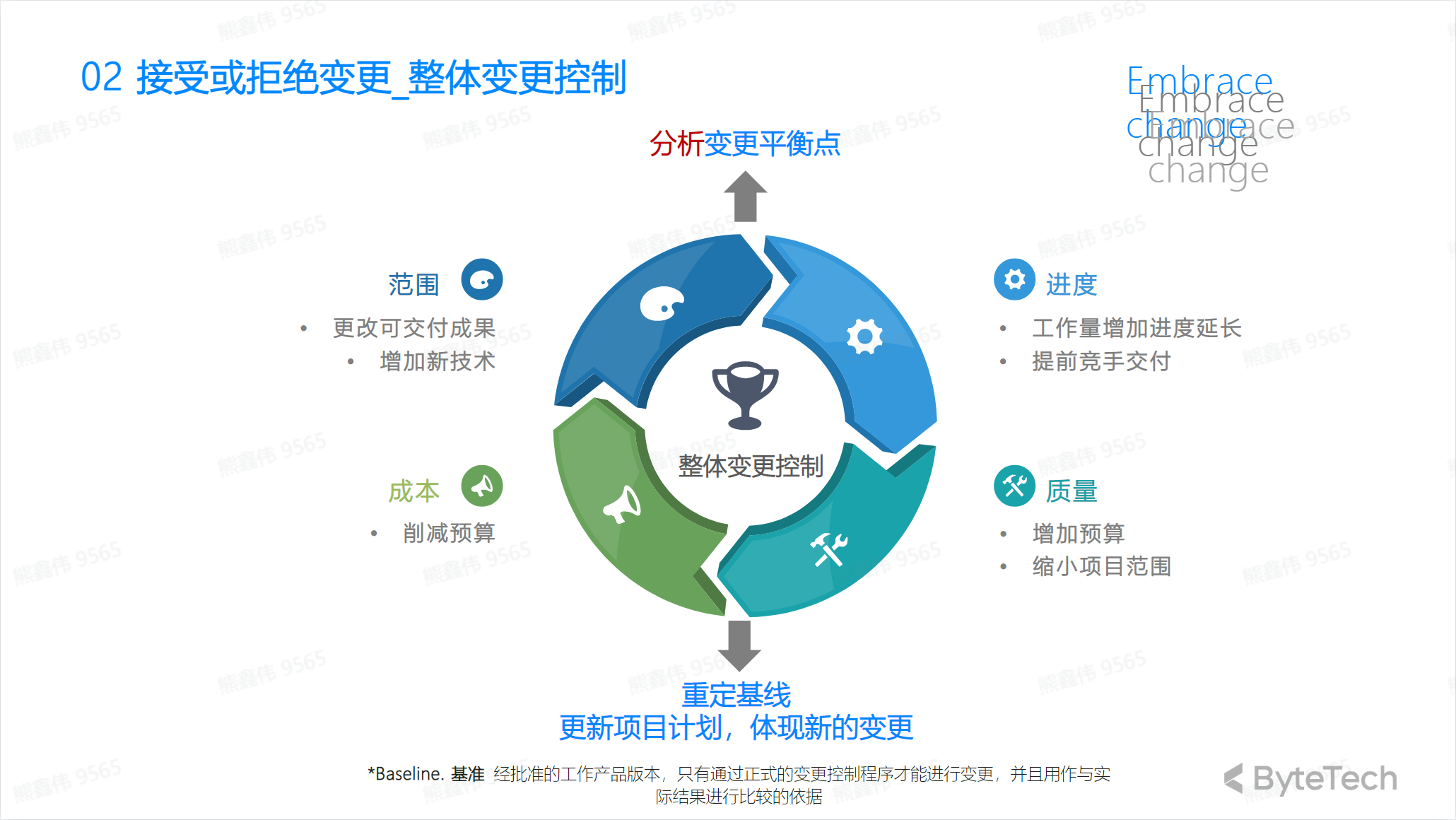
Overall change control
How to embrace change
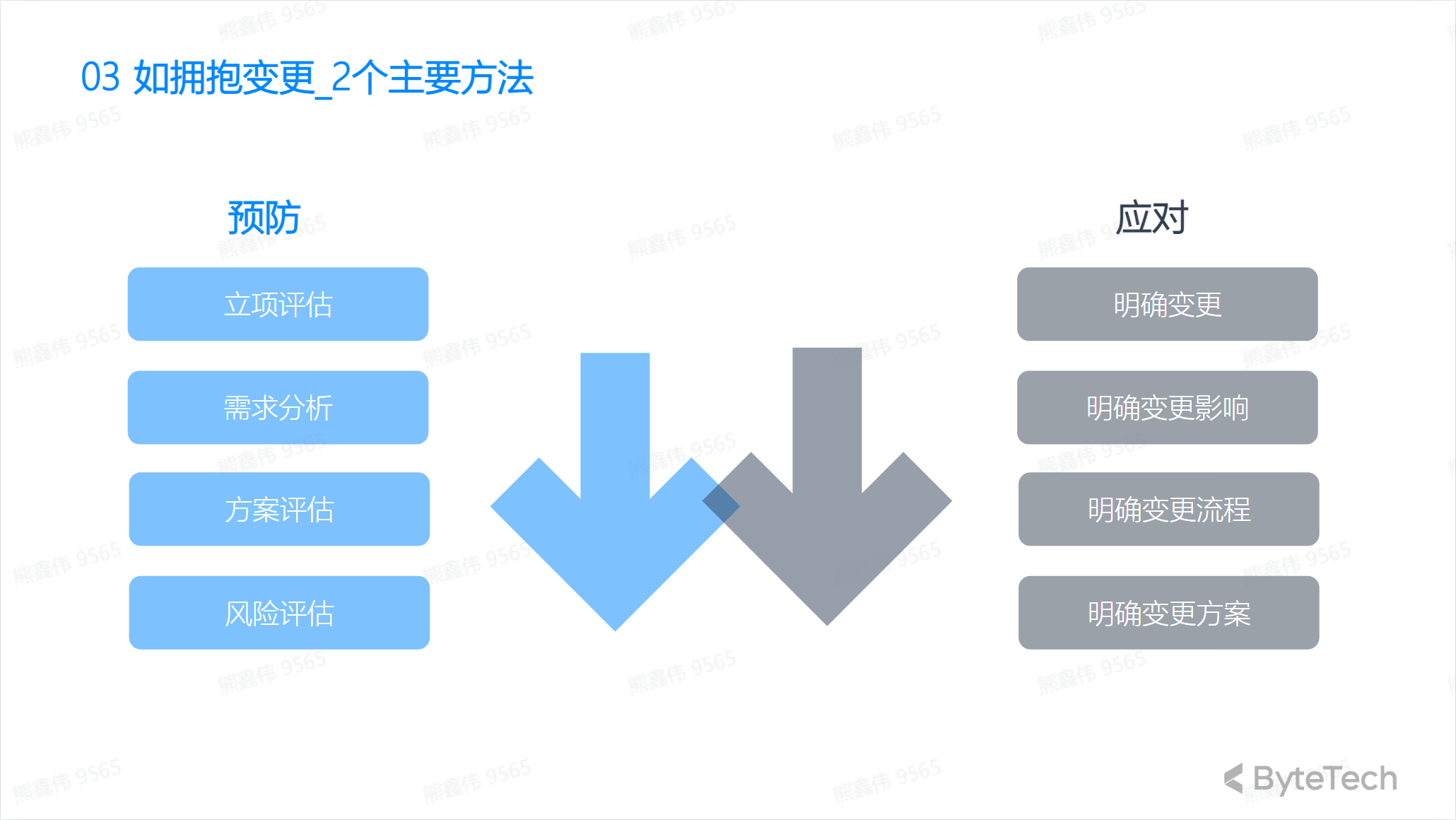
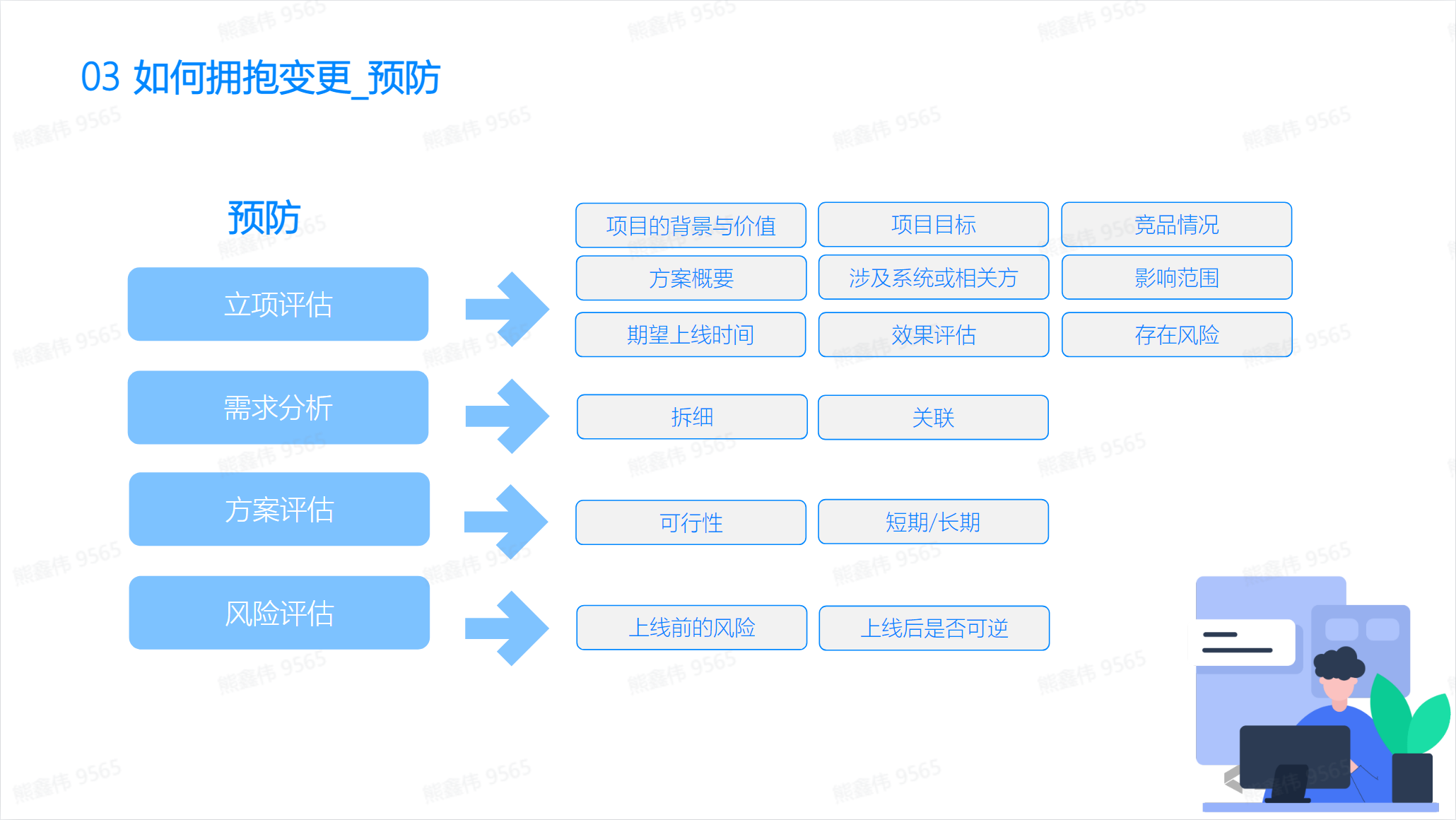
Prevention
Measures to prevent change include:
- Establish a flexible plan: The project manager should establish a flexible plan rather than a fixed plan so that it can cope with changes.
- Establish a risk management plan: The project manager should evaluate the risks that may arise in the project and establish an effective risk management plan.
- Frequently monitor project progress: Project managers should frequently monitor project progress, identify problems in a timely manner and take measures.
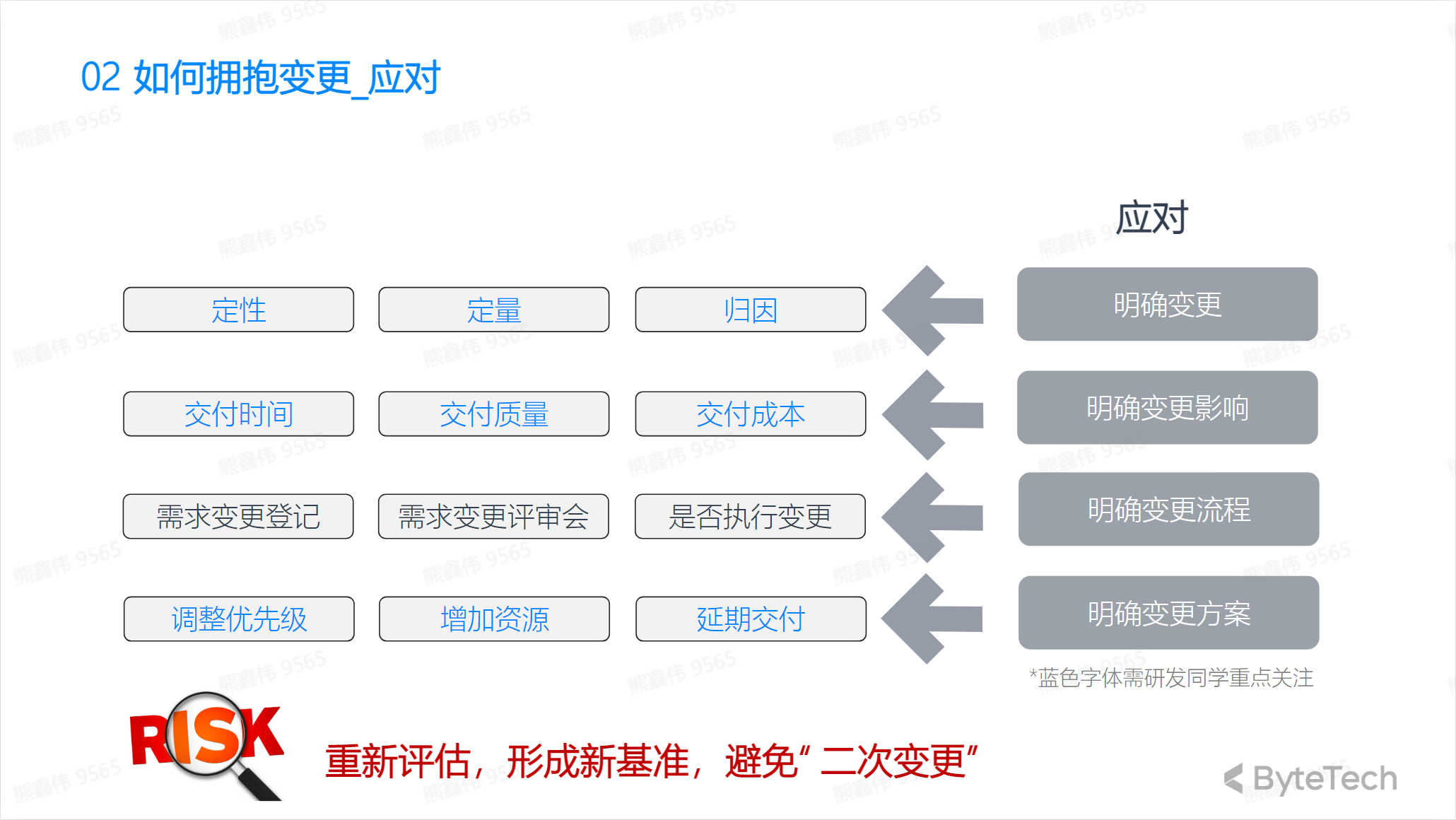
Response
Measures to respond to changes include:
- Change Control Procedure: The project manager should establish a change control procedure to ensure that changes are properly approved and managed.
- Adjust the plan: The project manager should be able to adjust the plan to accommodate changes.
- Coordinate the team: The project manager should coordinate the team to ensure that the changes are implemented correctly.
- Communication: The project manager should communicate the impact of the change to ensure that all relevant parties understand and support the change.
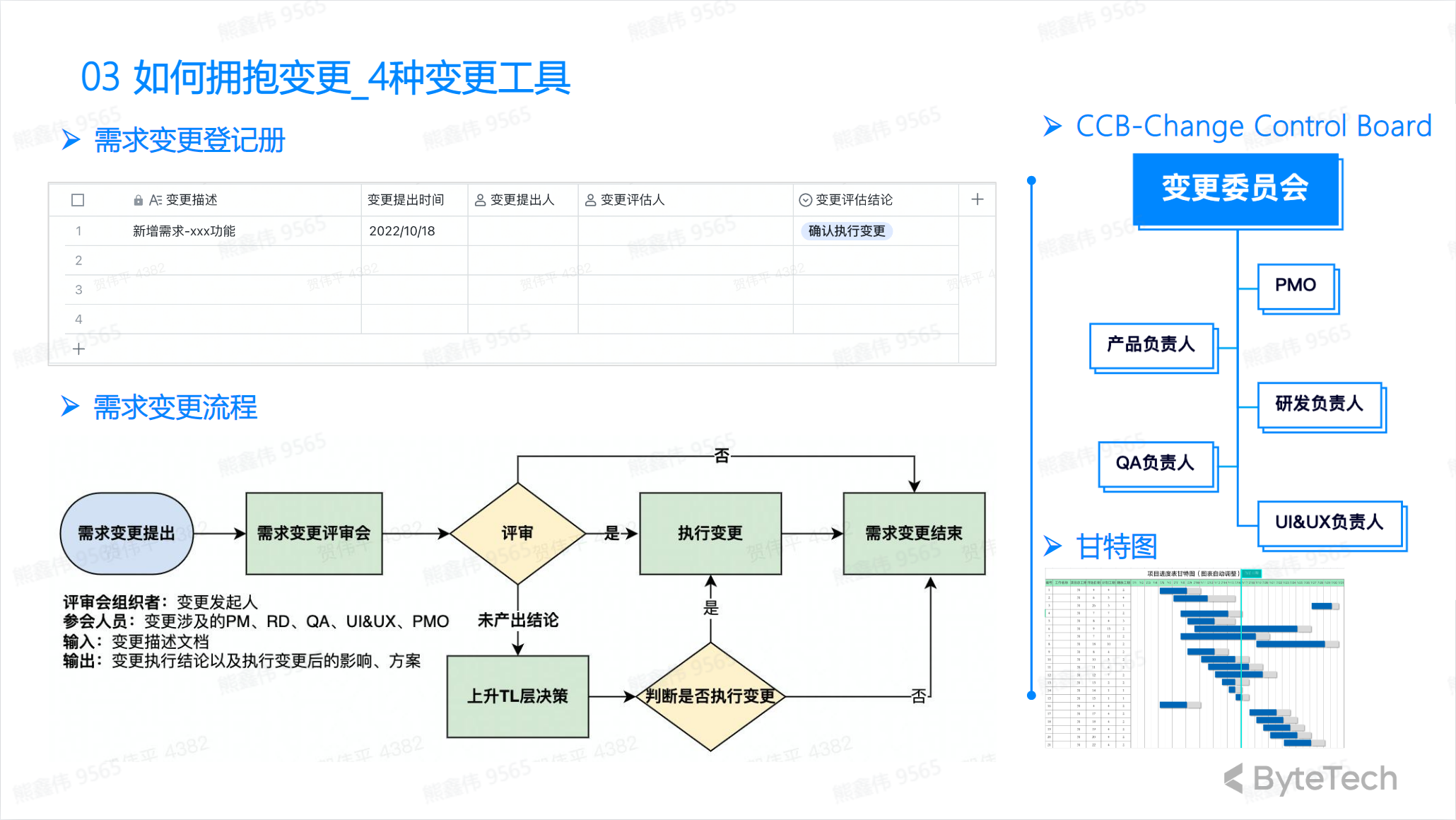
Four change tools
Monitoring: How to identify and respond to risks
🤸 **Risk is measurable uncertainty. **
**We saw above that monitoring occurs throughout the entire project life cycle. **

Risk Management Method
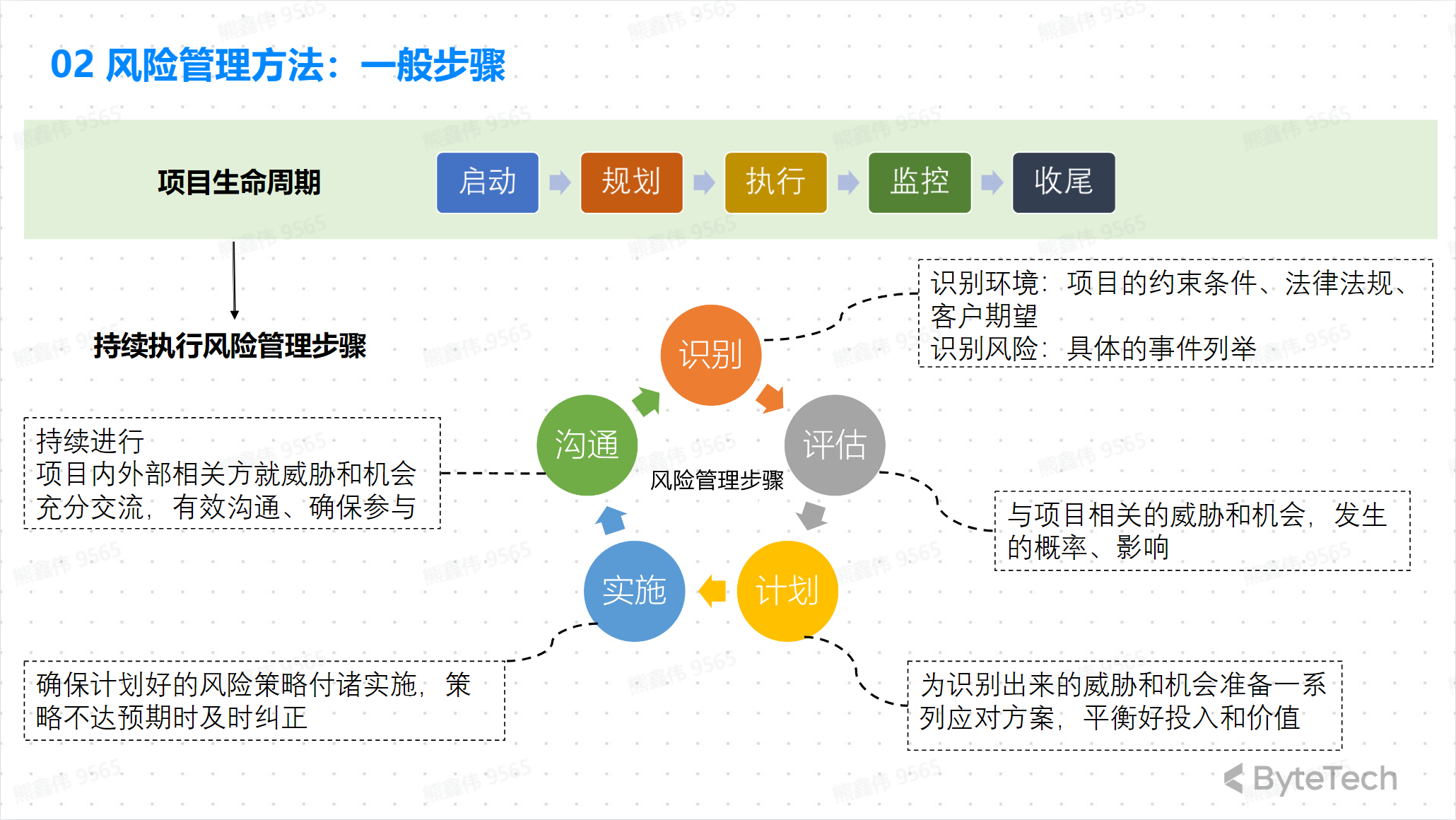
Risk Management Approach: Core


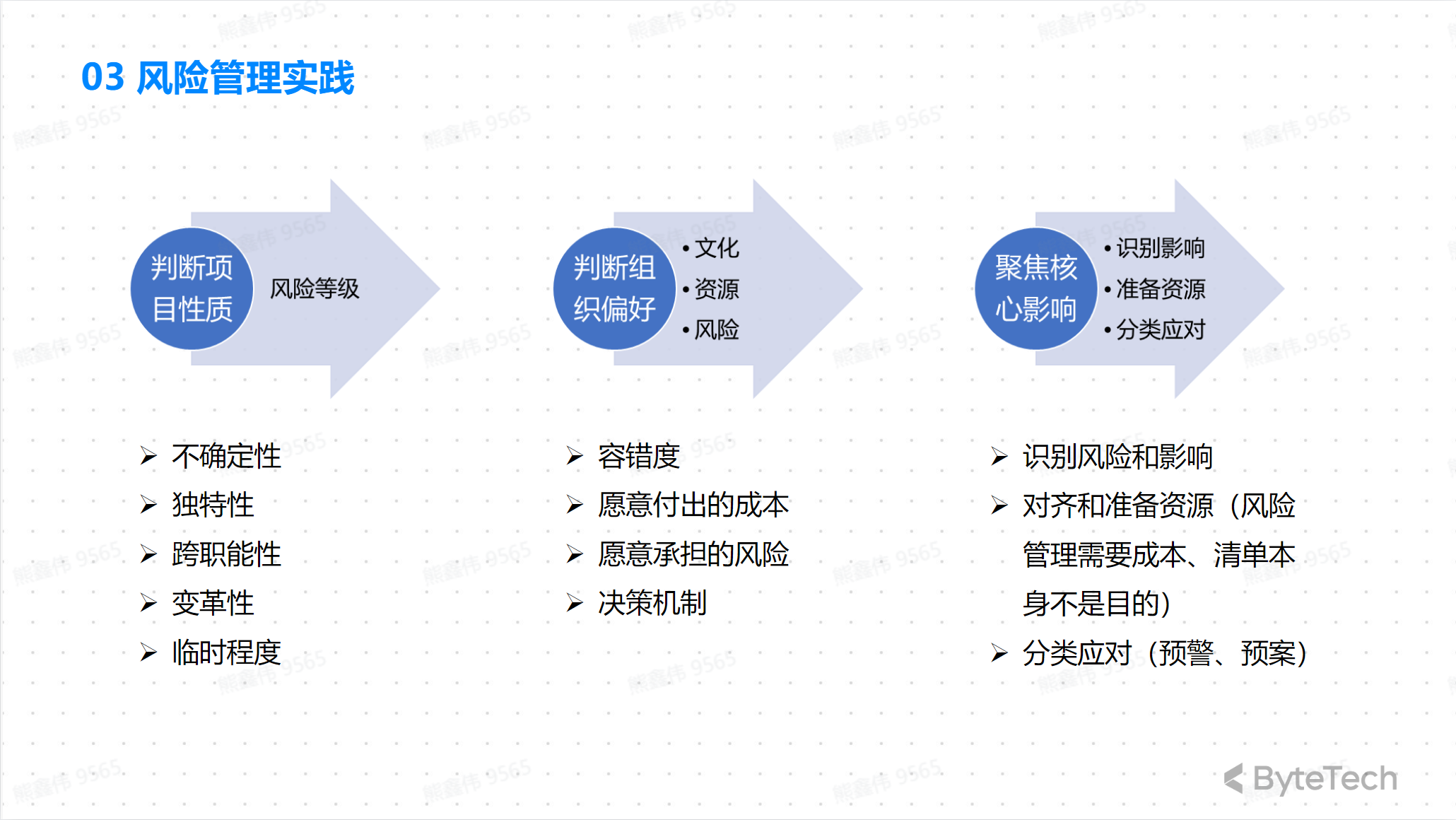
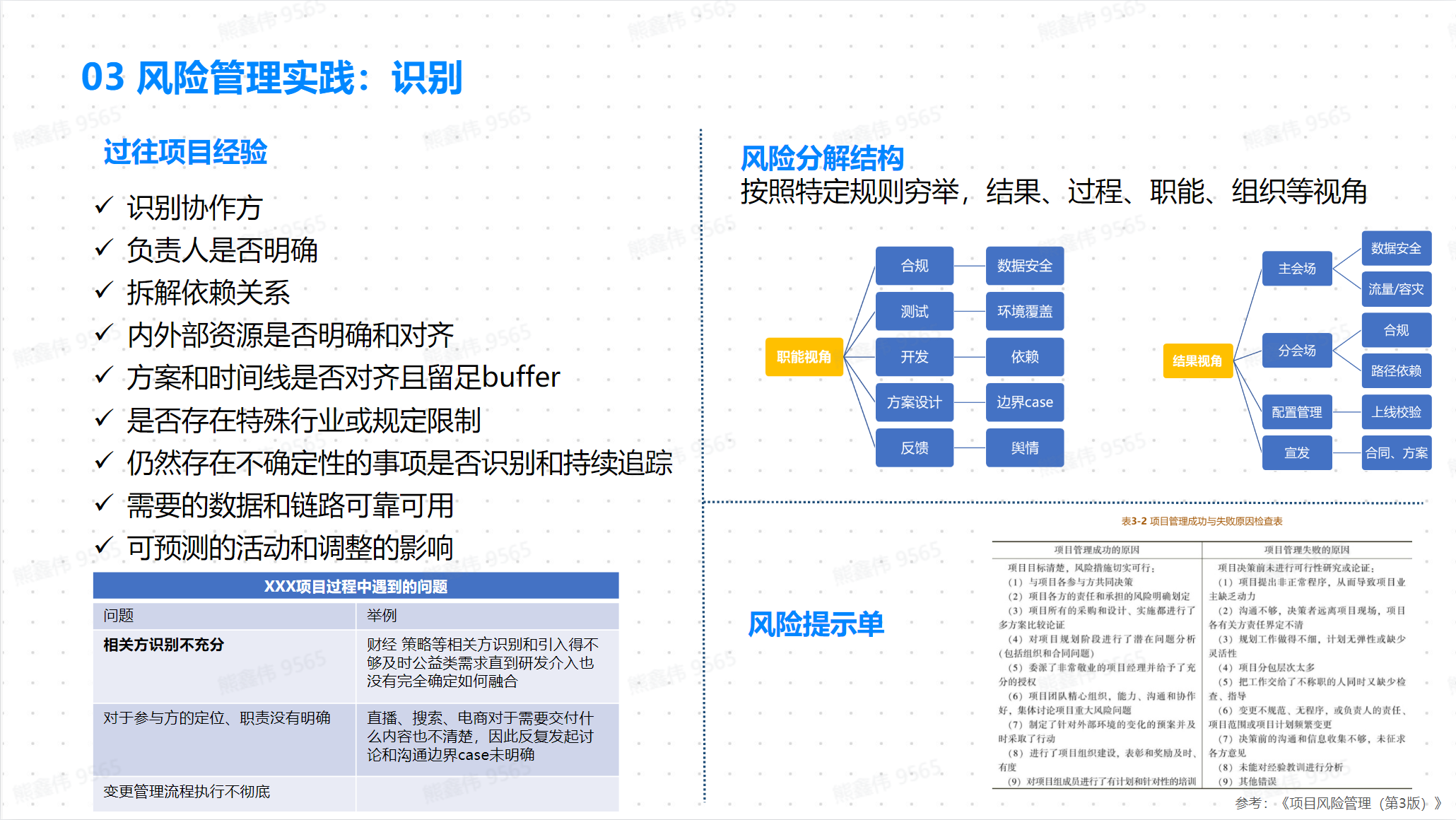
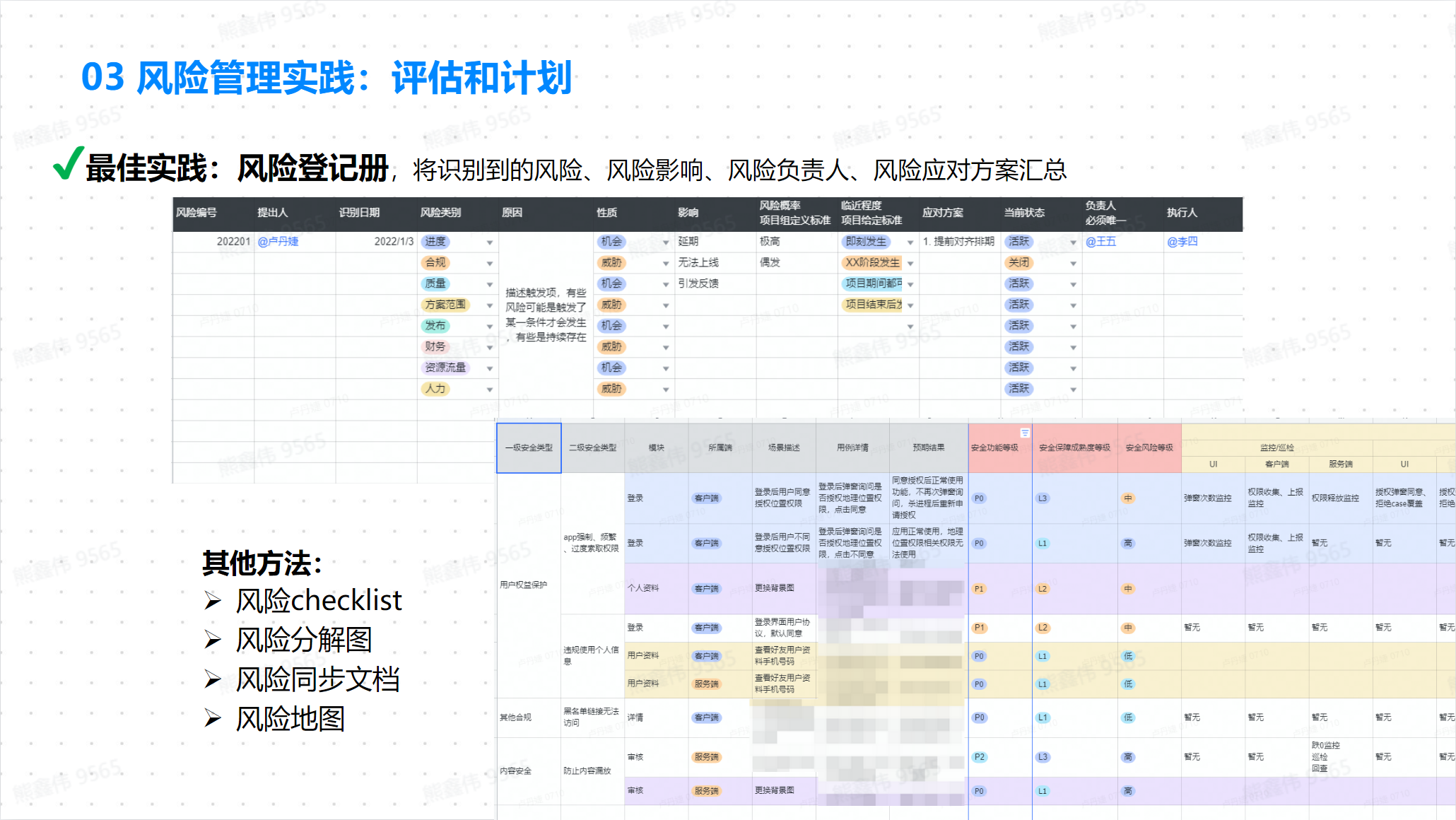
Risk Management Practice
Monitoring
Risk monitoring and early warning are important components of project management. Risk monitoring is the process of identifying new risks or updating known risks by regularly monitoring and evaluating the progress of a project. Risk warning is to issue warnings to relevant personnel so that corrective measures can be taken after new risks are discovered or known risks are updated.
Typically, risk monitoring and early warning tools include:
- Risk Daily: Daily or weekly submissions documenting new risks and updates to known risks
- Risk Matrix: a table used to track the probability and impact of risks
- Risk Tracking Software: Software for automatically tracking and reporting risks
Importantly, risk monitoring and early warning should be a continuous process to ensure that the project management team can take timely action to manage risks.

Implementation and communication
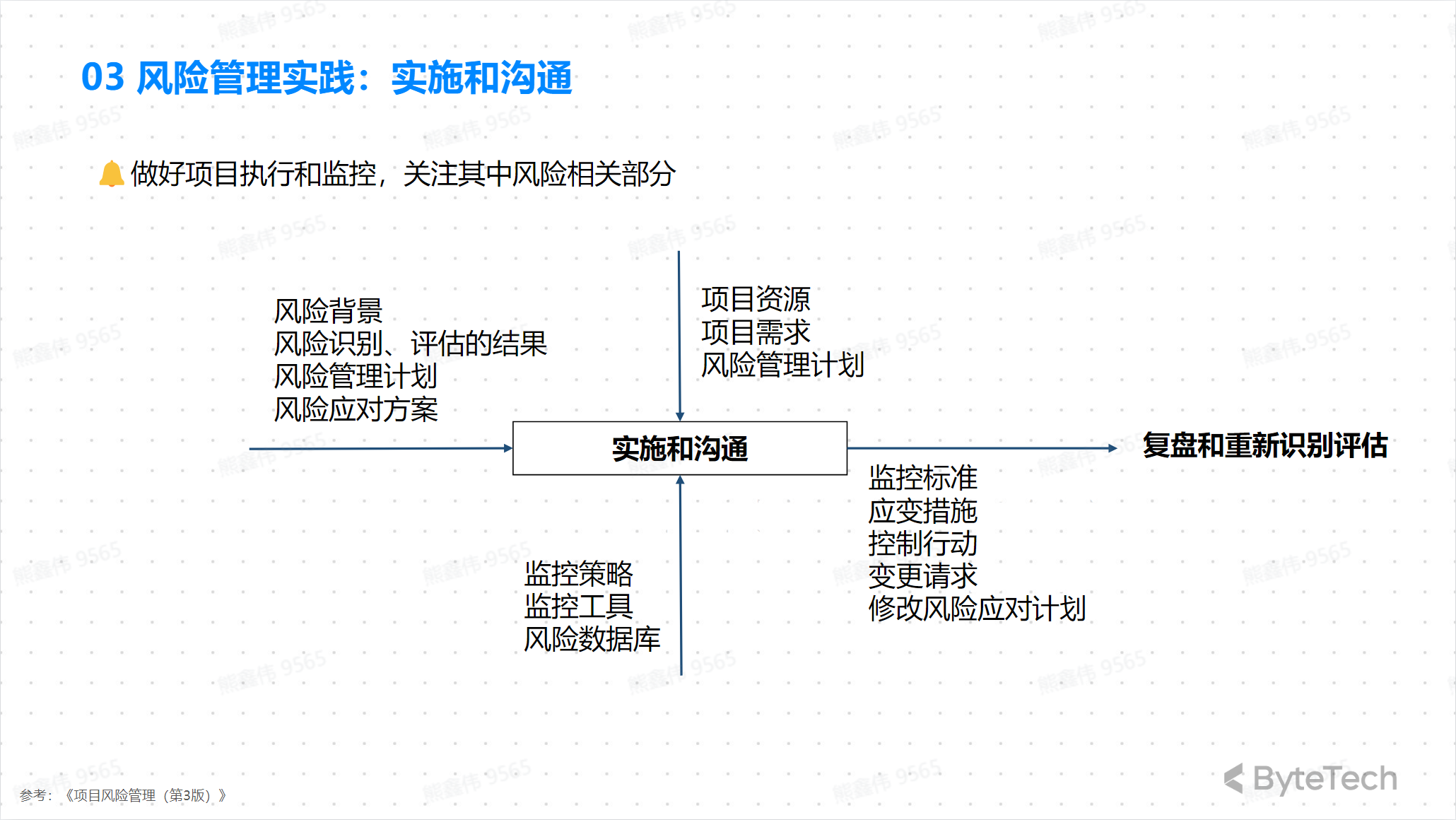
GitHub Project
Project Overview
As my most commonly used website, GitHub has endless functions.
Projects is an adaptable and flexible tool for planning and tracking work on GitHub.
Traditional project management in Github is carried out using issues and pull requests. This part is not the focus of this article and will not be discussed in detail. But there are some features that need to be mentioned:
- Tag: Different tags can be added to each issue, which can be used to mark the type of issue and the progress of issue processing;
- MileStone: Each issue belongs to only one milestone, which is used to display the issue processing progress.
Project provides real issue management capabilities; while the traditional tag method can only manually manage categories (such as Q&A, bug, duplicate, feature tags), or manually manage issue progress (need test, in progress) , wait approval and other tags).
**You can choose a high-density table layout or use the Kanban board function. **
Please read the corresponding github documentation: [https://docs.github.com/zh/enterprise-server@3.10/issues/planning-and-tracking-with-projects/customizing-views-in-your-project/changing-the -layout-of-a-view](https://docs.github.com/en/enterprise-server@3.10/issues/planning-and-tracking-with-projects/customizing-views-in-your-project/ changing-the-layout-of-a-view)
Kanban
Kanban management originated from Toyota’s production model and refers to a tool for controlling on-site production processes in order to achieve just-in-time (JIT) production. The pull production system in the just-in-time production method can shorten the information process, and cooperate with methods such as rationing and fixed loading containers to smooth the flow of materials in the production process.
KanbanFlow & Trello
It can be seen that the so-called Kanban board is to divide a wooden board into several columns, and then paste cards with different contents on each column. The columns on the board are generally in order, and cards can be moved between different columns to indicate their status.
In the above two examples, Kanban is not targeted at software engineering, and their market is also for general enterprises (such as Toyota).
Zenhub & Github Projects
The following two examples are optimized for software development. To be precise, they are adapted to Github.
- Zenhub is a browser plug-in that treats Github issues as cards and displays issues in the form of Kanban. It provides a relatively tasteless Epic function, and also has TODO item management for individuals.
- The Project recently launched by Github can not only use issues as cards, but also Notes (the three on the left), so that we do not need to create a new issue or record the issue in order to record possible requirements on the board. On my personal TODO list.
Github Projects
**Why Projects? ** A repository can contain multiple projects; at first, this setting made me confused. It was not until I used it that I realized that a code repository usually has many things to do, such as:
Prepare route map
- Add a new function
- Release a new version
Therefore, we can create a Project for each of the above things. Since there is no Epic-like mechanism in Github, it is useful to use different Projects.
It can be seen that with Project’s Kanban, some of the original tag functions (such as tag processing progress, etc.)Can be replaced by Kanban. Notes provided by Github Project can be individually converted into issues when needed:
At the same time, Kanban can not only contain issues and notes, but also pull requests.
Github finally has a more reliable project management tool, and open source projects have better tools. Sprinkle flowers o(^▽^)o
I wish myself to complete my first open source project (IMAP Server) as soon as possible.
Example explanation
GitHub is currently one of the largest open source centers in the world, and many people manage their own open program codes on it. The built-in Issue function is also very convenient, where you can put forward areas that need improvement/enhancement. But for project developers, management is a little more inconvenient, especially in an era when billboard management is becoming more and more popular, and listed Issues will appear to be messy and difficult to manage. There are also many third-party companies that have launched billboard functions integrated with GitHub, but management is always a little inconvenient, so GitHub also decided to launch a built-in billboard function─Projects! It allows you to easily integrate the current Issues/Pull Requests into the billboard. Although the overall function of the billboard is relatively bright, the basic functions are also available, and the operation method is similar to the functions of the currently popular billboard software, and for Direct integration with GitHub is really convenient! Next, I will use a small project I am currently working on, 8ComicDownloaderElectron, to introduce the billboard function on GitHub!
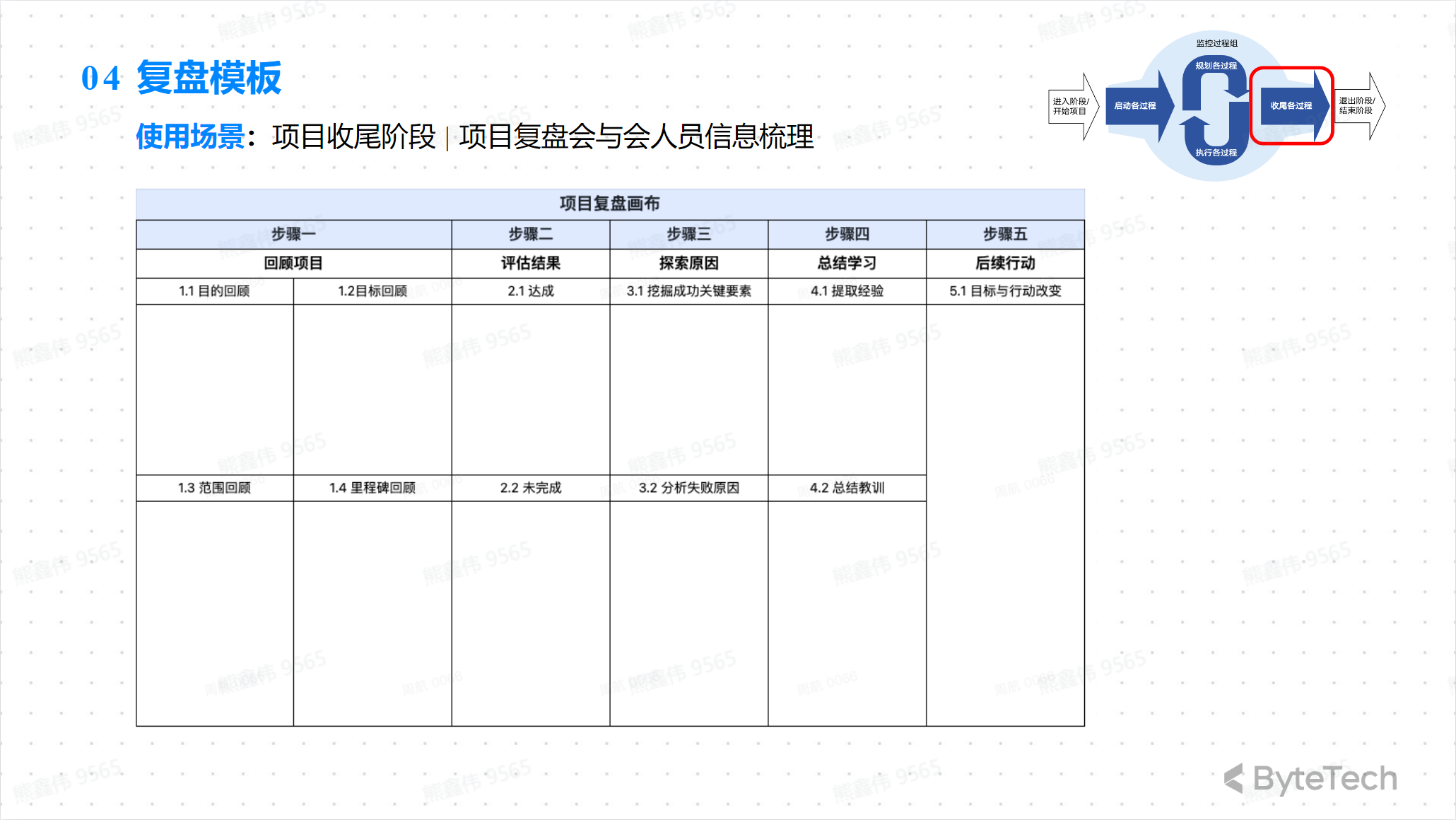
Closing: Efficient review
**Project review is an evaluation process conducted after the end of the project. The purpose is to summarize the results and lessons learned from the project and make improvements for future projects. **
Project review steps include:
- Organize a project review meeting: Invite project team members, relevant department managers, project committee members, etc. to the meeting.
- Organize project data: Collect project documents, data and records.
- Summarize the project results: Evaluate the project results, including whether the project goals are achieved, and whether the project quality, cost and time meet expectations.
- Summarize the lessons learned from the project: Evaluate the lessons learned from the project, including the problems that occurred during the project and how to solve these problems.
- Develop an improvement plan: Based on the results of the project review, develop an improvement plan to improve the success rate of future projects.
Project review is an important part of project management. It can help project management teams and organizations improve the project management process and increase the success rate of future projects.
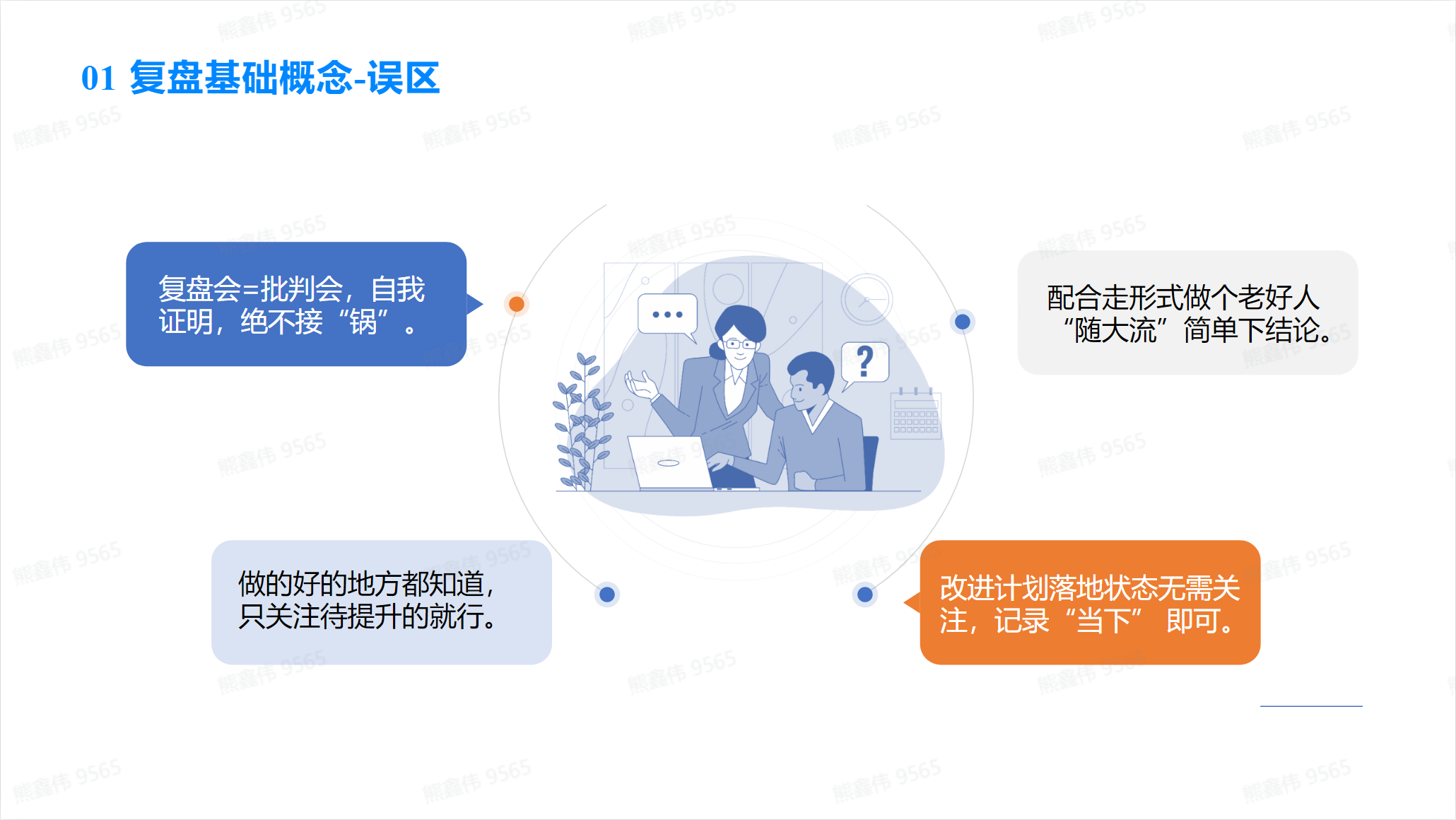
Introduction to basic concepts of review
The review process for small projects and large projects is basically similar, but there may be some differences in implementation.
- The review of small projects may be simpler and more flexible. A simple summary and evaluation can be carried out after the project is completed, and the review process can be completed in a short time. You don’t need too many participants, just the project manager and project members.
- The review of large projects is more complex and may take longer to complete. Project managers need to collect large amounts of data and documents and conduct detailed assessments. There are also more participants, and project team members, relevant department managers, project committee members, etc. may be needed.

Review attitude
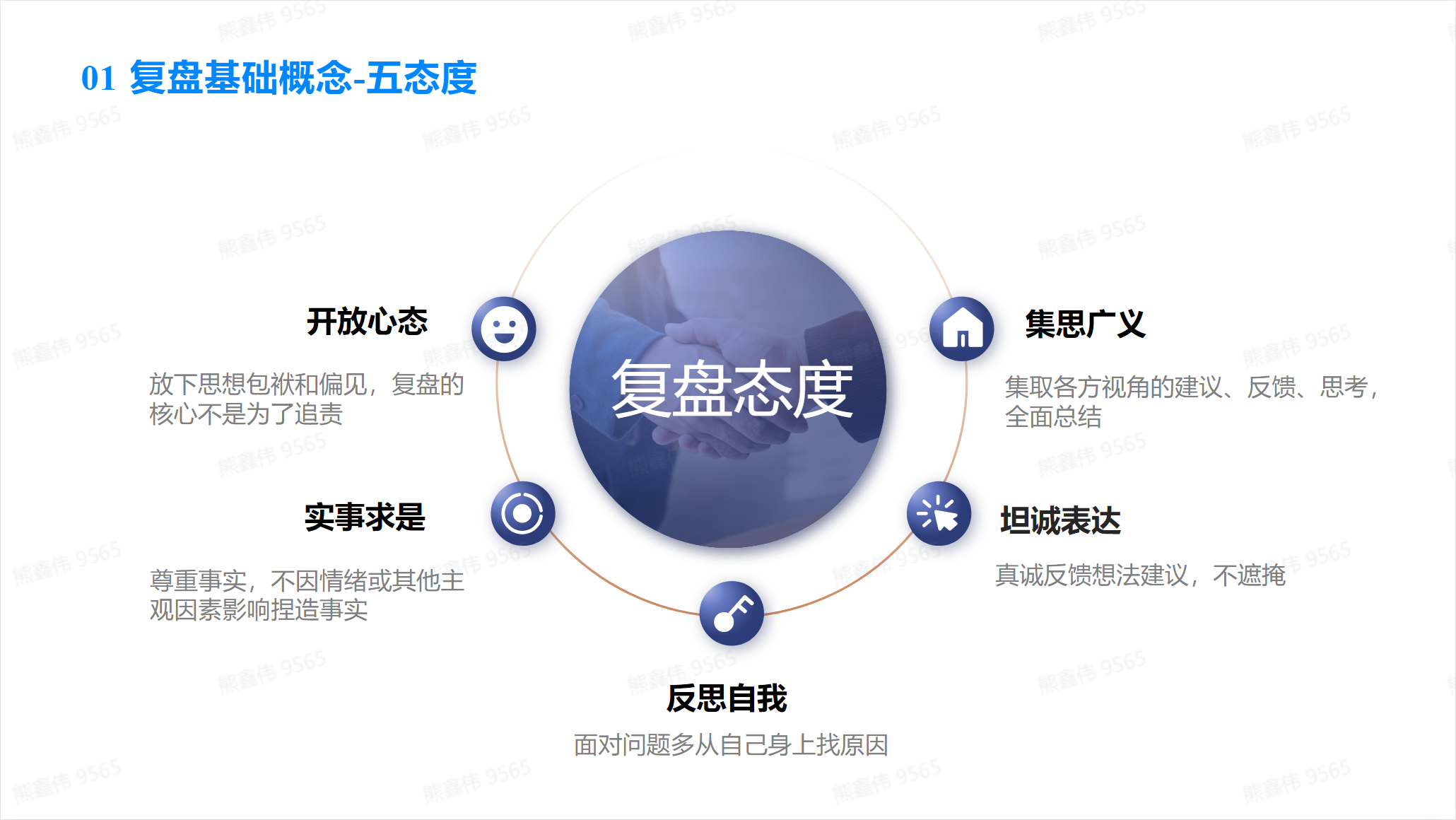
Four steps of review

The corresponding💡simple case is as follows:

Review steps:
- Plan the review: Arrange the review meeting, identify participants, and prepare necessary documents and data.
- Collect information: Collect project documents, data and records, including project plans, project performance indicators, project progress reports, etc.
- Analyze information: Analyze project data and documents to evaluate project results and benefits.
- Summary of the project: Summarize the project results and lessons learned, evaluate the problems that occurred in the project, and formulate an improvement plan.
- Record results: Record the results of the review, including project results, lessons learned and improvement plans, and share them with relevant personnel.
- Implement improvement plans: Act on improvement plans to increase the success rate of future projects.
Review is a continuous process that continuously summarizes the progress of the project and develops improvement plans to improve the efficiency and success rate of the project.

Review case analysis

Recommended practical project management tools
Directory:
| Document name | Document link | |—————- | ———————————- - | | Project basic information table | Project basic information table | | Core Member List | Core Member List | | Milestone Chart | Milestone Chart | | Version Rhythm Table | Version Rhythm Table | | Project Communication Plan | Project Communication Plan | | tracker-Gantt chart | tracker-Gantt chart | | Risk Register | Risk Register | | Problem Register | Problem Register | | Meeting Minutes | Meeting Minutes | | Project Phase Report | Project Phase Report I Project Phase Report II | | Program phase reports | Program phase reports | | Review Template | Review Template |
Onepage template—project basic information table
Usage scenario: Project startup planning stage | Project background, goals, and expected revenue specification

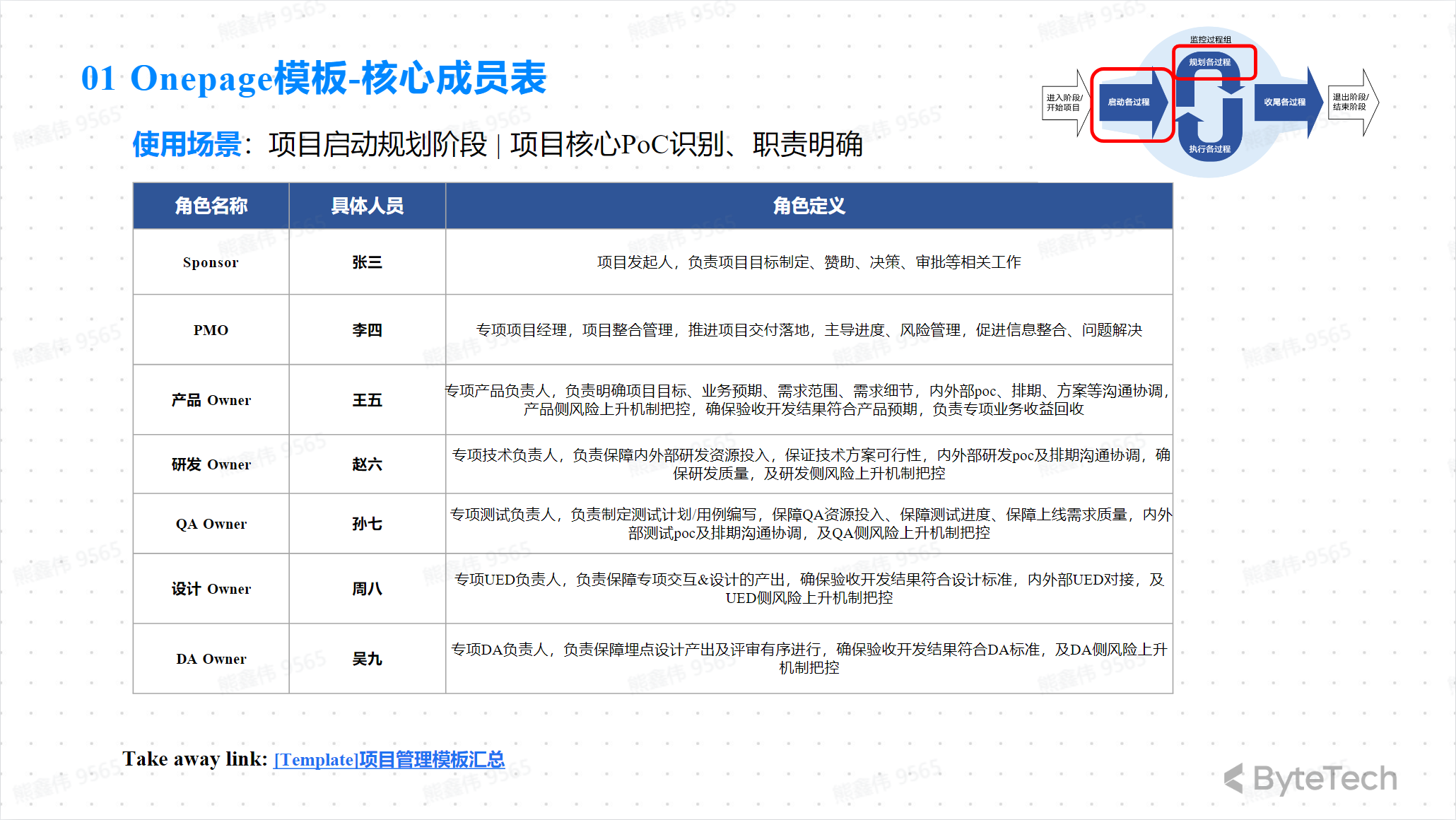
Onepage template—core member table
Onepage Template—Milestone Chart
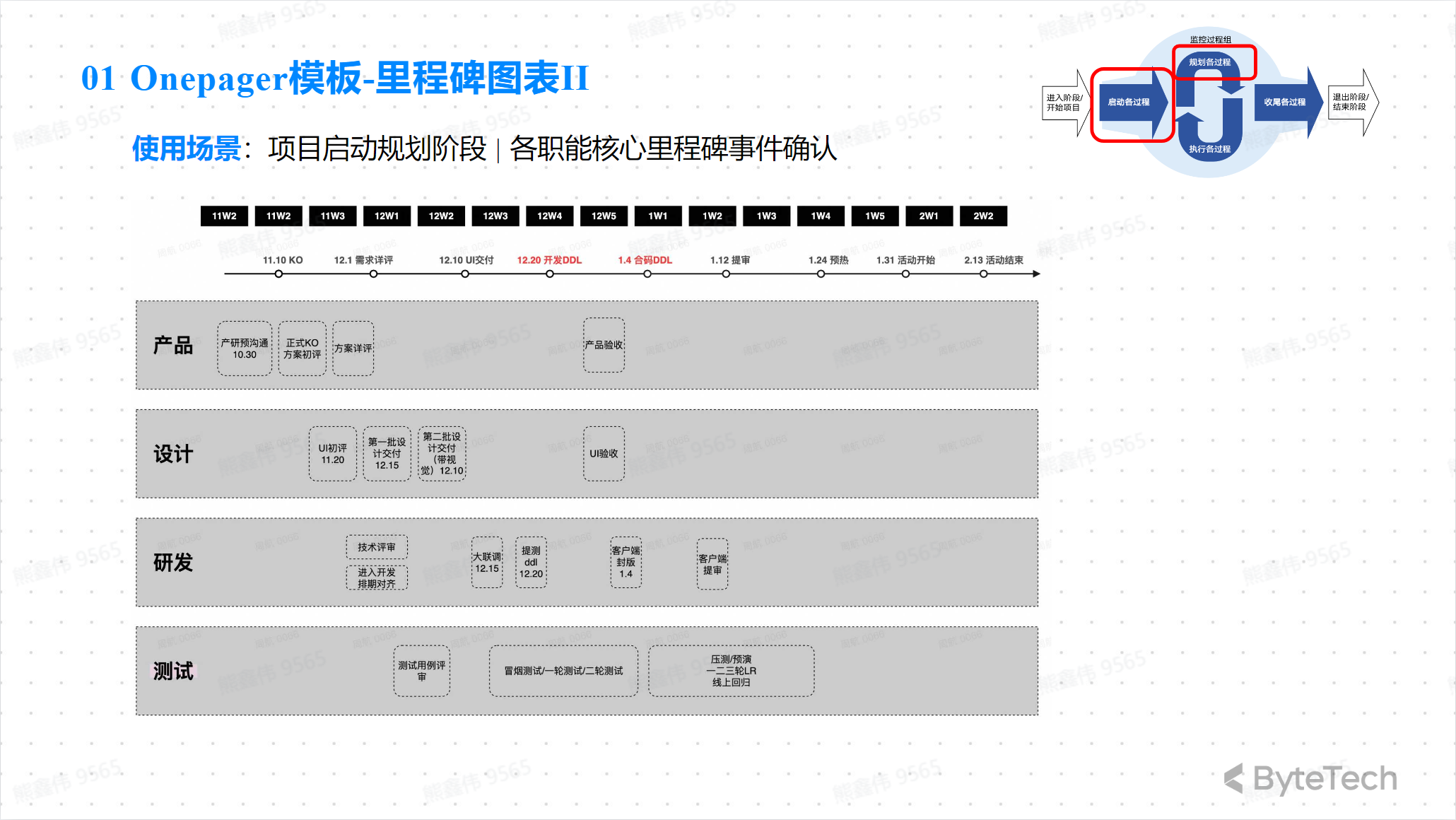
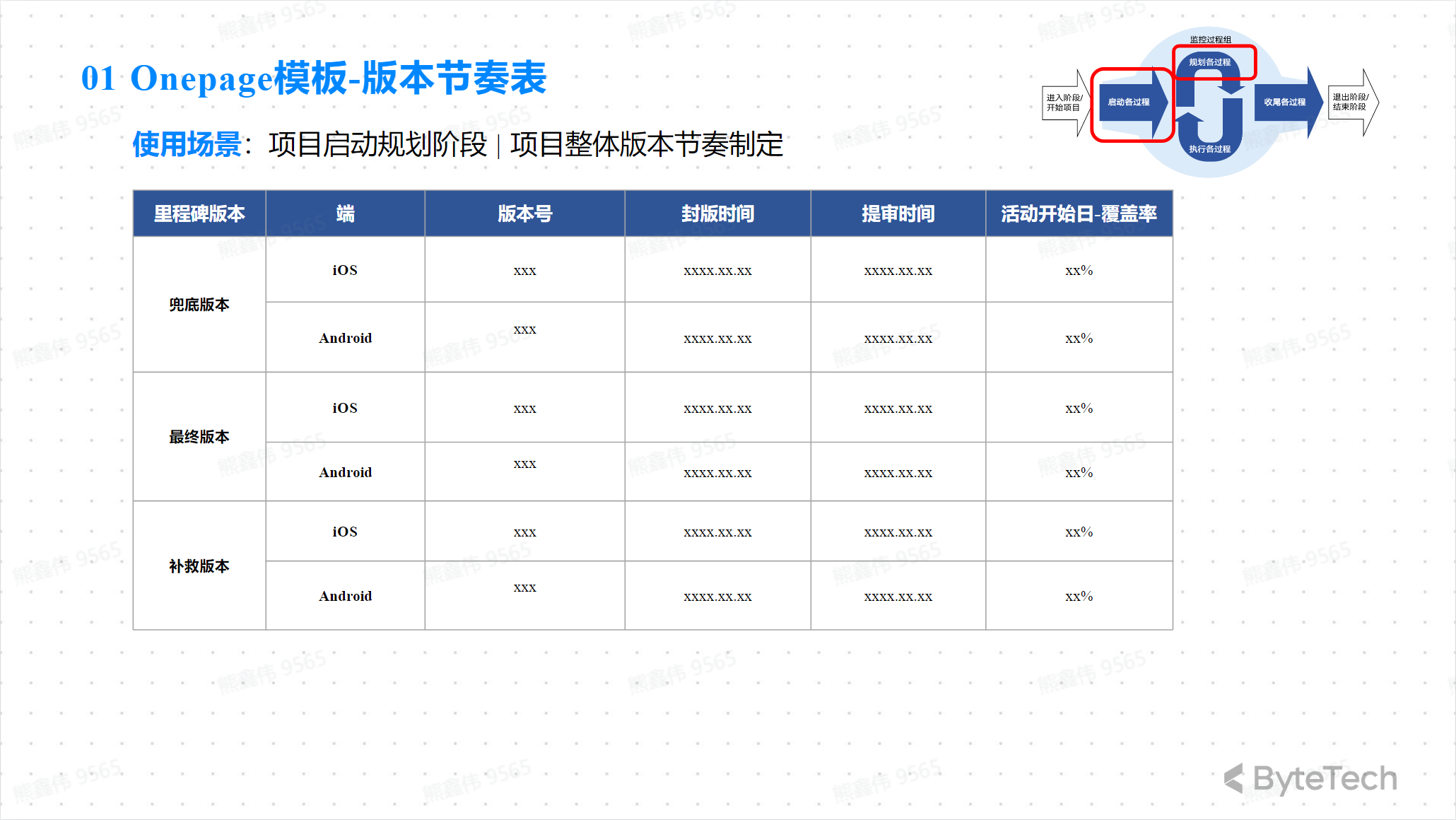
Onepage Template—Project Communication Plan

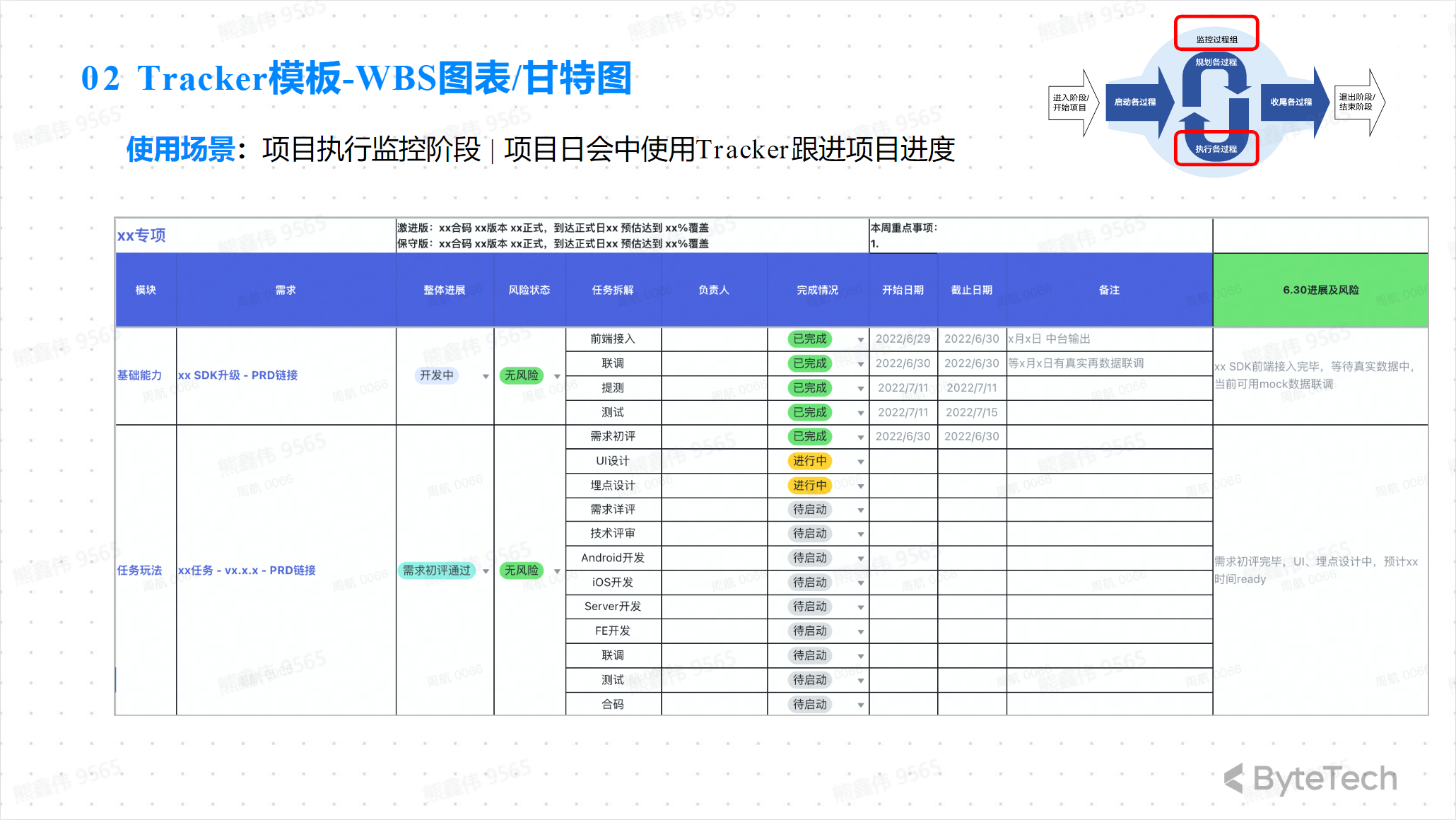
Tracker Template—WBS/Gantt Chart
Tracker Template—Risk Registration Form
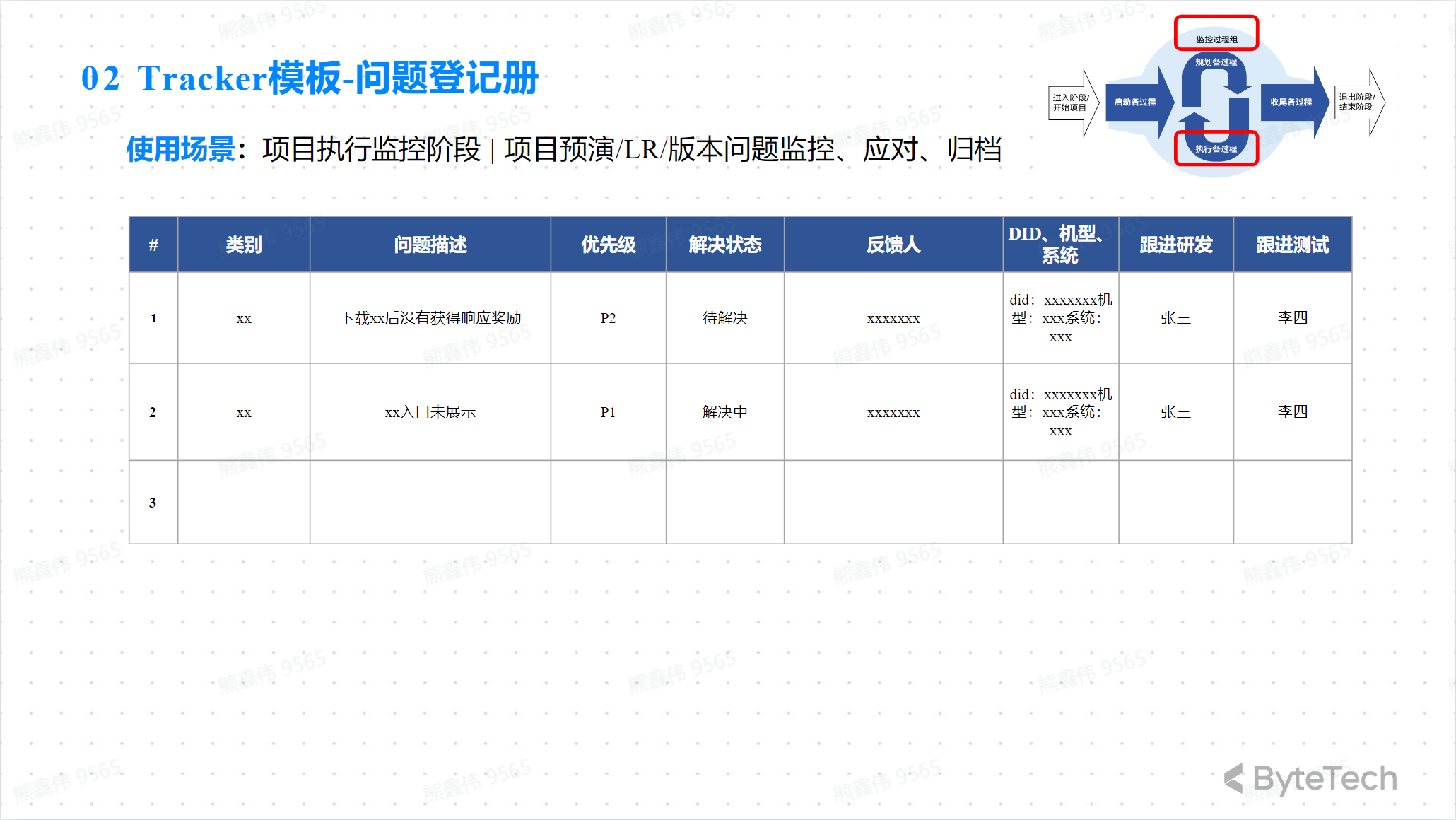
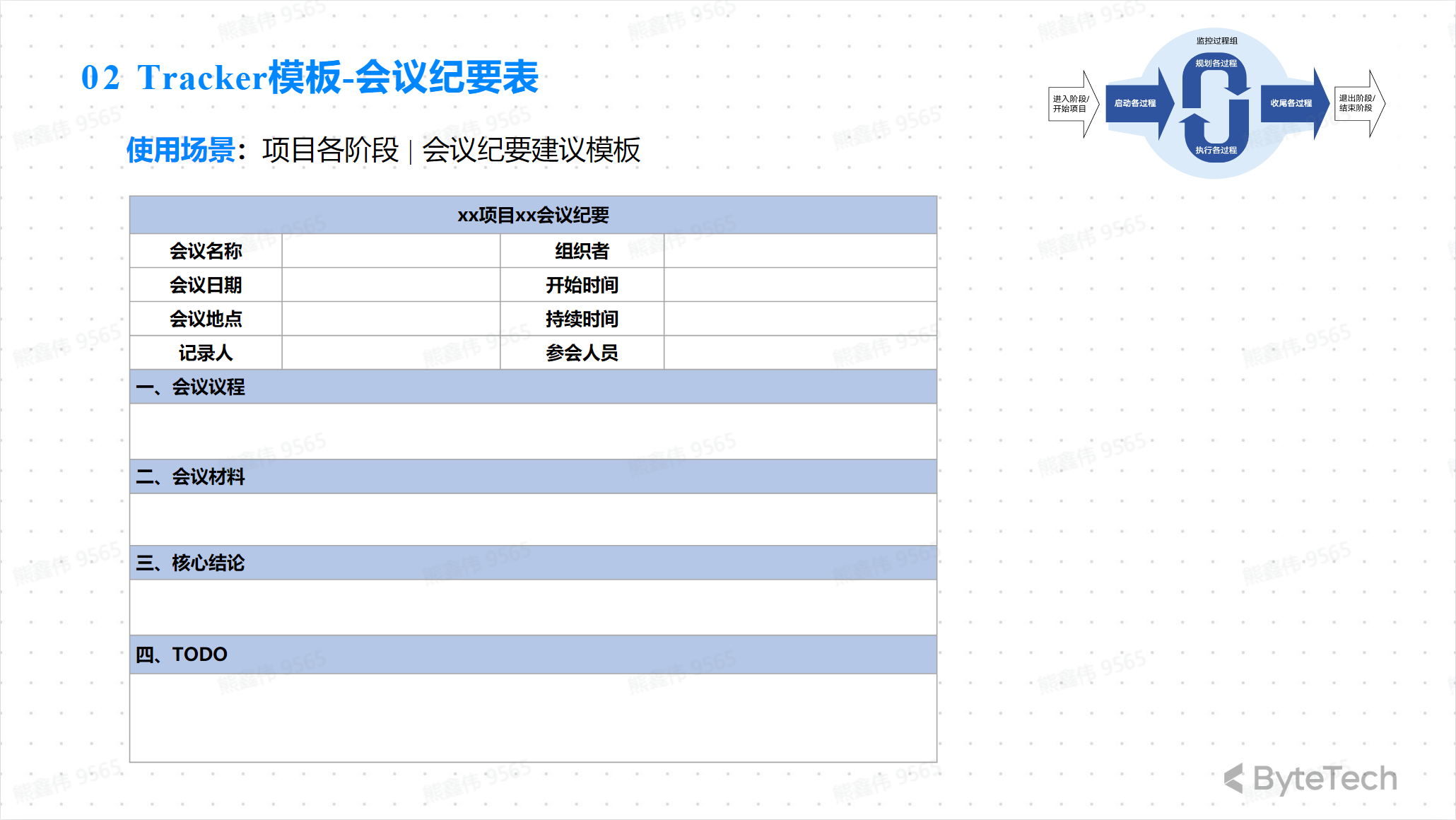
Tracker Template—Meeting Minutes
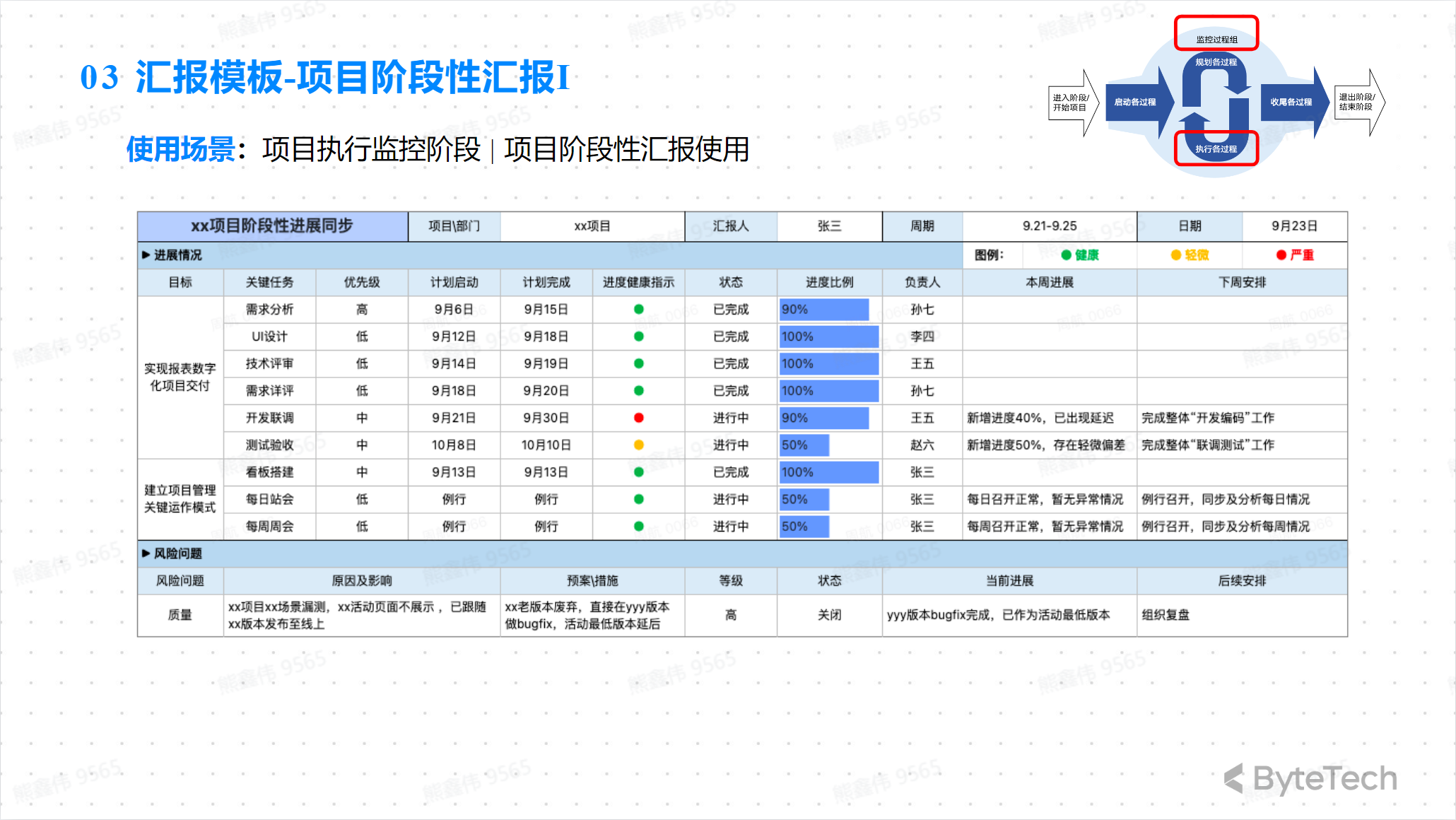
Project Report Form—Phase Report 1
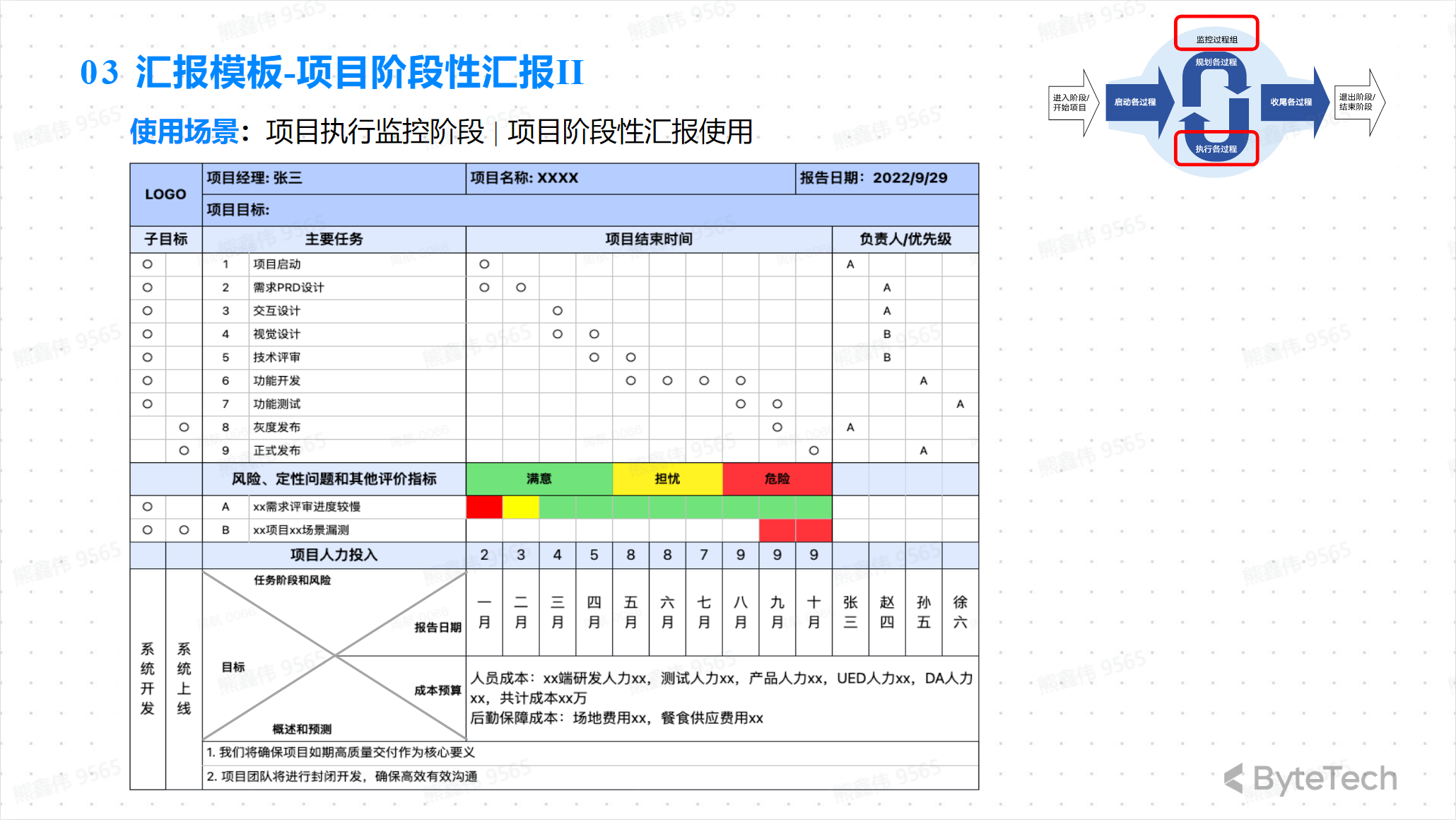
Project Report Form—Phase Report 2
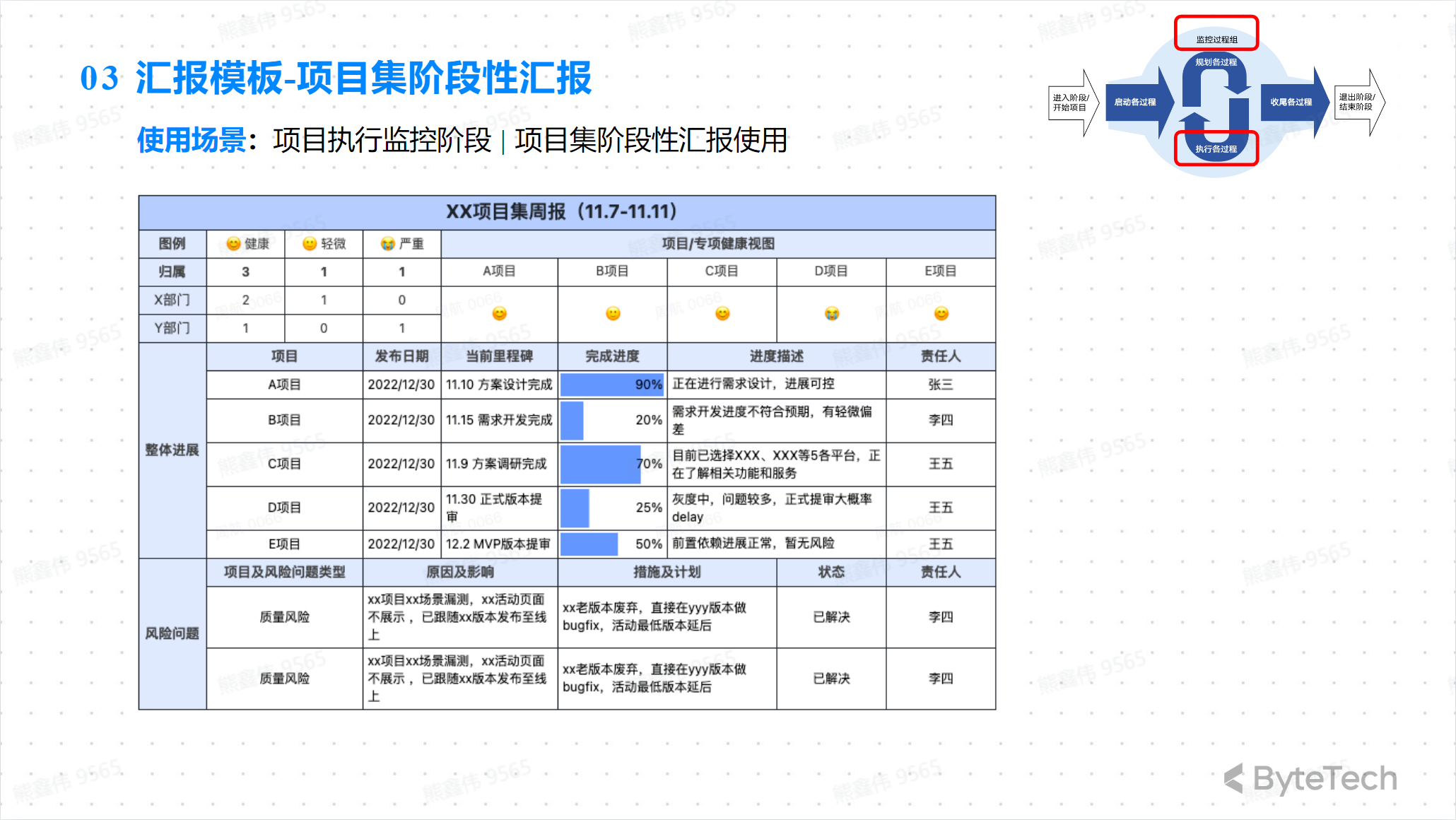
###Project stage report
Review template